MQTT Protocol
MQTT is a machine-to-machine (M2M)/"Internet of Things" connectivity protocol.
It was designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport.
It is useful for connections with remote locations where a small code footprint is required and/or network bandwidth is at a premium.
IoTDB supports the MQTT v3.1(an OASIS Standard) protocol.
IoTDB server includes a built-in MQTT service that allows remote devices send messages into IoTDB server directly.
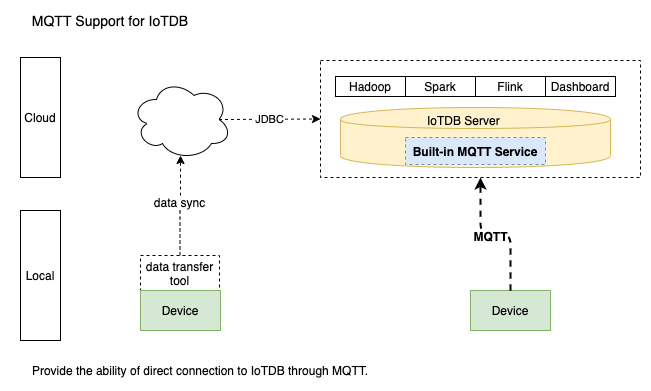
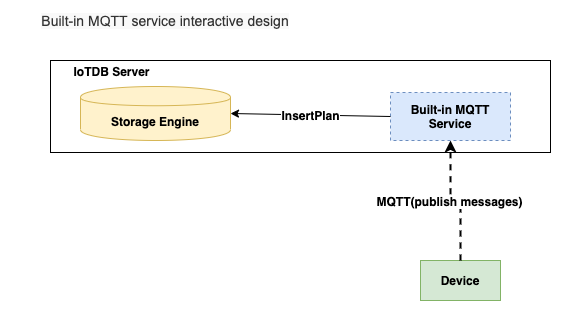
Built-in MQTT Service
The Built-in MQTT Service provide the ability of direct connection to IoTDB through MQTT. It listen the publish messages from MQTT clients
and then write the data into storage immediately.
The MQTT topic corresponds to IoTDB timeseries.
The messages payload can be format to events by PayloadFormatter which loaded by java SPI, and the default implementation is JSONPayloadFormatter.
The default json formatter support two json format, and the following is an MQTT message payload example:
{
"device":"root.sg.d1",
"timestamp":1586076045524,
"measurements":["s1","s2"],
"values":[0.530635,0.530635]
}or
{
"device":"root.sg.d1",
"timestamps":[1586076045524,1586076065526],
"measurements":["s1","s2"],
"values":[[0.530635,0.530635], [0.530655,0.530695]]
}
MQTT Configurations
The IoTDB MQTT service load configurations from ${IOTDB_HOME}/${IOTDB_CONF}/iotdb-engine.properties by default.
Configurations are as follows:
| NAME | DESCRIPTION | DEFAULT |
|---|---|---|
| enable_mqtt_service | whether to enable the mqtt service | false |
| mqtt_host | the mqtt service binding host | 0.0.0.0 |
| mqtt_port | the mqtt service binding port | 1883 |
| mqtt_handler_pool_size | the handler pool size for handing the mqtt messages | 1 |
| mqtt_payload_formatter | the mqtt message payload formatter | json |
| mqtt_max_message_size | the max mqtt message size in byte | 1048576 |
Coding Examples
The following is an example which a mqtt client send messages to IoTDB server.
MQTT mqtt = new MQTT();
mqtt.setHost("127.0.0.1", 1883);
mqtt.setUserName("root");
mqtt.setPassword("root");
BlockingConnection connection = mqtt.blockingConnection();
connection.connect();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String payload = String.format("{\n" +
"\"device\":\"root.sg.d1\",\n" +
"\"timestamp\":%d,\n" +
"\"measurements\":[\"s1\"],\n" +
"\"values\":[%f]\n" +
"}", System.currentTimeMillis(), random.nextDouble());
connection.publish("root.sg.d1.s1", payload.getBytes(), QoS.AT_LEAST_ONCE, false);
}
connection.disconnect();Customize your MQTT Message Format
If you do not like the above Json format, you can customize your MQTT Message format by just writing several lines
of codes. An example can be found in example/mqtt-customize project.
Steps:
- Create a java project, and add dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.iotdb</groupId>
<artifactId>iotdb-server</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>- Define your implementation which implements
org.apache.iotdb.db.mqtt.PayloadFormatter.java
e.g.,
package org.apache.iotdb.mqtt.server;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import org.apache.iotdb.db.protocol.mqtt.Message;
import org.apache.iotdb.db.protocol.mqtt.PayloadFormatter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomizedJsonPayloadFormatter implements PayloadFormatter {
@Override
public List<Message> format(ByteBuf payload) {
// Suppose the payload is a json format
if (payload == null) {
return null;
}
String json = payload.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// parse data from the json and generate Messages and put them into List<Meesage> ret
List<Message> ret = new ArrayList<>();
// this is just an example, so we just generate some Messages directly
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
long ts = i;
Message message = new Message();
message.setDevice("d" + i);
message.setTimestamp(ts);
message.setMeasurements(Arrays.asList("s1", "s2"));
message.setValues(Arrays.asList("4.0" + i, "5.0" + i));
ret.add(message);
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
// set the value of mqtt_payload_formatter in iotdb-engine.properties as the following string:
return "CustomizedJson";
}
}- modify the file in
src/main/resources/META-INF/services/org.apache.iotdb.db.mqtt.PayloadFormatter:
clean the file and put your implementation class name into the file.
In this example, the content is:org.apache.iotdb.mqtt.server.CustomizedJsonPayloadFormatter - compile your implementation as a jar file:
mvn package -DskipTests
Then, in your server:
- put the jar into your server's lib folder
- Update configuration to enable MQTT service. (
enable_mqtt_service=trueinconf/iotdb-engine.properties) - Set the value of
mqtt_payload_formatterinconf/iotdb-engine.propertiesas the value of getName() in your implementation
, in this example, the value isCustomizedJson - Launch the IoTDB server.
- Now IoTDB will use your implementation to parse the MQTT message.
More: the message format can be anything you want. For example, if it is a binary format,
just use payload.forEachByte() or payload.array to get bytes content.
