AINode
AINode
AINode is a native IoTDB node designed for registering, managing, and invoking time series-related models. It integrates industry-leading self-developed time series large models—such as the Timer series developed by Tsinghua University—and supports millisecond-level real-time inference on time series data via standard SQL statements. It enables key application scenarios including time series trend forecasting, missing value imputation, and anomaly detection.
System architecture is illustrated below:
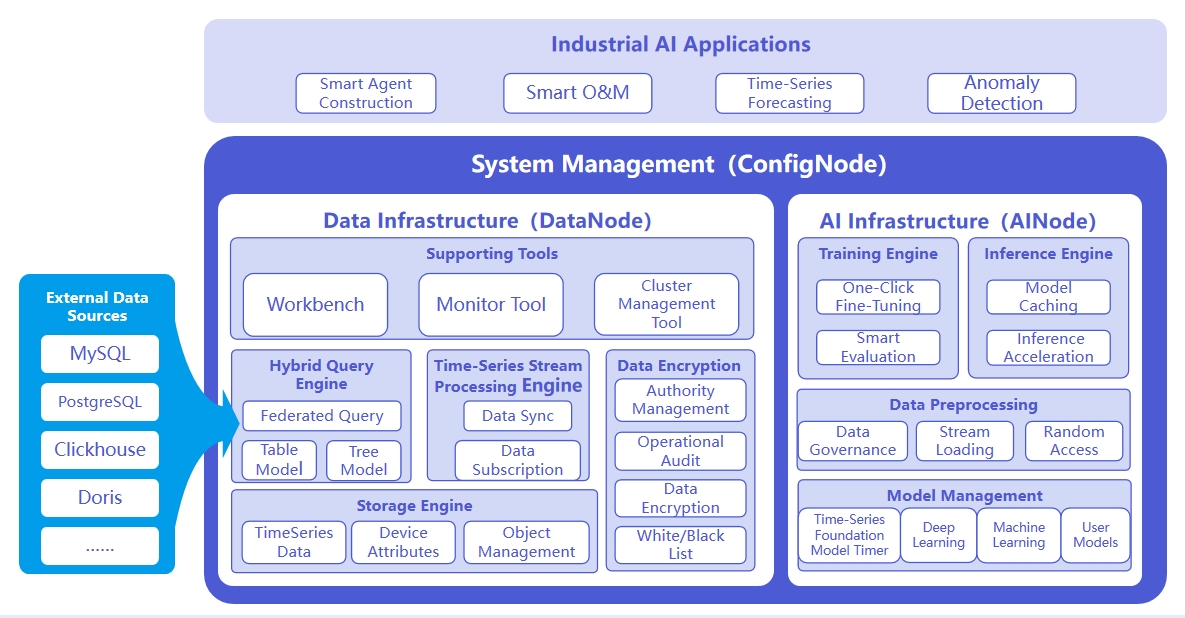
Responsibilities of the three node types are as follows:
- ConfigNode: Manages distributed nodes and handles load balancing.
- DataNode: Receives and parses user SQL requests; stores time series data; performs data preprocessing computations.
- AINode: Manages and utilizes time series models.
1. Advantages and Features
Compared to building a standalone machine learning service, AINode offers the following benefits:
- Ease of Use: No Python or Java programming required. Complete model management and inference workflows are achievable via SQL statements. For example, use
CREATE MODELto register a model andSELECT * FROM FORECAST (...)for inference—simple and efficient. - Eliminates Data Migration: IoTDB-native machine learning enables direct inference on data stored within IoTDB, avoiding data transfer to external ML platforms. This accelerates processing, enhances security, and reduces costs.
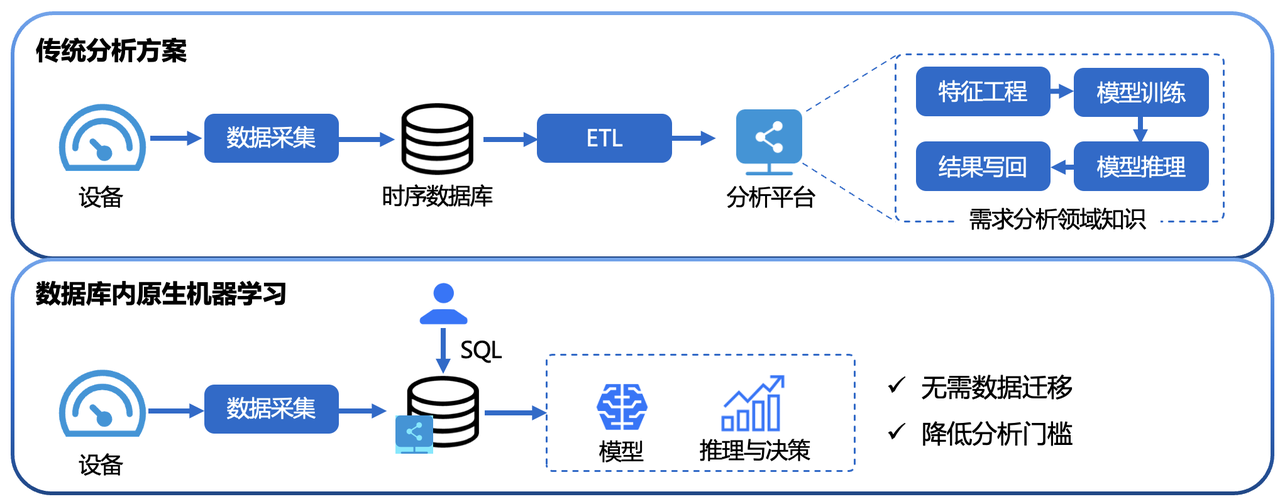
- Built-in Advanced Algorithms: Integrates state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms covering typical time series analysis tasks, empowering IoTDB with native analytical capabilities:
- Time Series Forecasting: Learns patterns from historical sequences to predict future values based on past observations.
- Anomaly Detection for Time Series: Detects and identifies outliers in time series data to uncover abnormal behaviors.
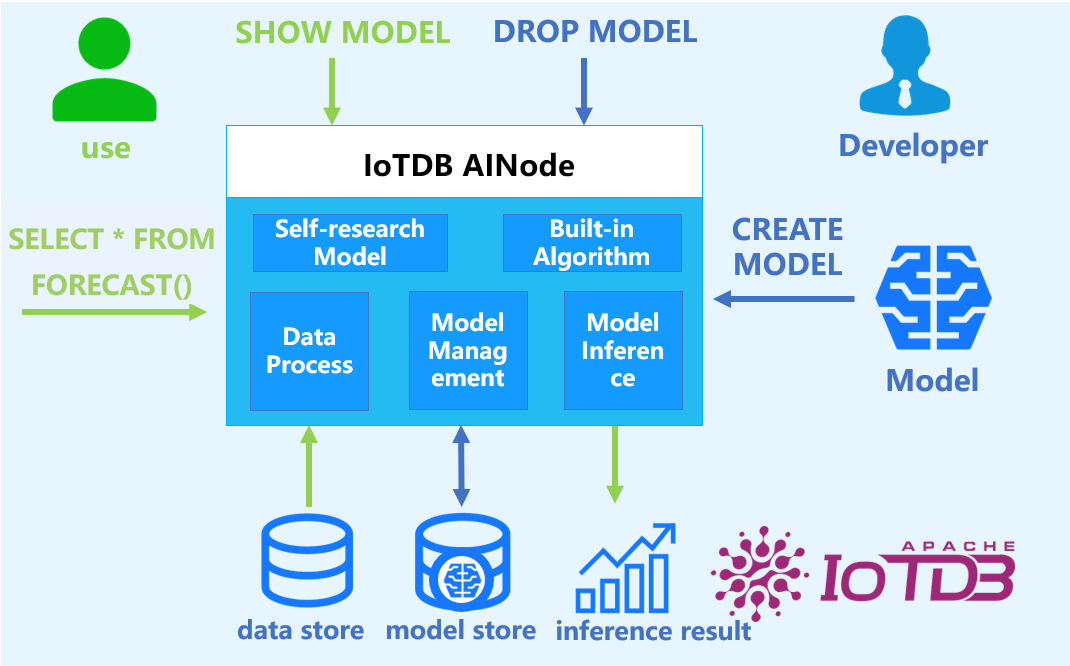
2. Core Concepts
- Model: A machine learning model that takes time series data as input and outputs analytical results or decisions. Models are the fundamental management units in AINode, supporting creation (registration), deletion, querying, and inference.
- Create: Loads externally designed or trained model files/algorithms into AINode for unified management and usage.
- Inference: Applies a registered model to perform time series analysis tasks on specified data.
- Built-in Capability: AINode includes native algorithms/models for common time series scenarios (e.g., forecasting and anomaly detection).
3. Installation and Deployment
Refer to the documentation AINode Deployment for deployment instructions.
4. Usage Guide
AINode supports two core functionalities: model inference and model management (registration, viewing, deletion, loading, unloading). Details follow.
4.1 Model Inference
AINode supports forecasting inference on single target variables. Syntax, parameters, and examples are provided below.
- SQL Syntax
SELECT * FROM FORECAST(
MODEL_ID,
TARGETS, -- SQL to retrieve target variables
OUTPUT_START_TIME,
OUTPUT_LENGTH,
OUTPUT_INTERVAL,
TIMECOL,
PRESERVE_INPUT,
[MODEL_OPTIONS]?
)- Built-in models require no registration. Specify
model_idin theforecastfunction to invoke inference. - Parameter Description
| Parameter Name | Type | Attribute | Description | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model_id | Scalar | String | Unique identifier of the forecasting model | Yes | |
| targets | Table | SET SEMANTIC | Input data for target variables. IoTDB automatically sorts data by time before sending to AINode | Yes | Invalid SQL in this clause triggers query errors |
| output_start_time | Scalar | Timestamp. Default: last timestamp of targets + output_interval | Start timestamp of forecast output (issue time) | No | Must be later than the maximum timestamp in targets |
| output_length | Scalar | INT32. Default: 96 | Output window size | No | Must be > 0 |
| output_interval | Scalar | Interval. Default: (last_ts - first_ts) / (n - 1) | Time interval between forecast points (units: ns, us, ms, s, m, h, d, w) | No | Must be > 0 |
| timecol | Scalar | String. Default: "time" | Name of the time column | No | Must exist in targets and be of TIMESTAMP type |
| preserve_input | Scalar | Boolean. Default: false | Whether to retain all original input rows in output | No | |
| model_options | Scalar | String. Default: empty string | Model-specific key-value pairs (e.g., normalization settings); separated by ';' | No |
Notes:
- Default Behavior: Forecasts all columns in
targets. Currently supports INT32, INT64, FLOAT, DOUBLE types only. - Input Requirements:
- Must include a time column.
- Row count: Errors if below minimum; truncates to latest rows if exceeding maximum.
- Output:
- Contains all target variable columns with original data types.
- If
preserve_input=true, adds anis_inputcolumn to mark original rows.
- Timestamp Generation:
- Uses
OUTPUT_START_TIME(optional) as forecast start point. - Uses
OUTPUT_INTERVAL(optional, defaults to input sampling interval). Timestamp of row N:OUTPUT_START_TIME + (N - 1) * OUTPUT_INTERVAL.
- Uses
- Usage Example
Create database etth and table eg:
CREATE DATABASE etth;
CREATE TABLE eg (hufl FLOAT FIELD, hull FLOAT FIELD, mufl FLOAT FIELD, mull FLOAT FIELD, lufl FLOAT FIELD, lull FLOAT FIELD, ot FLOAT FIELD)Prepare source data ETTh1-tab
Forecast 96 future values of sensor ot using its latest 96 historical records:
IoTDB:etth> SELECT Time, HUFL, HULL, MUFL, MULL, LUFL, LULL, OT FROM eg LIMIT 96
+-----------------------------+------+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+------+
| Time| HUFL| HULL| MUFL| MULL| LUFL| LULL| OT|
+-----------------------------+------+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+------+
|2016-07-01T00:00:00.000+08:00| 5.827|2.009|1.599|0.462|4.203| 1.34|30.531|
|2016-07-01T01:00:00.000+08:00| 5.693|2.076|1.492|0.426|4.142|1.371|27.787|
|2016-07-01T02:00:00.000+08:00| 5.157|1.741|1.279|0.355|3.777|1.218|27.787|
|2016-07-01T03:00:00.000+08:00| 5.09|1.942|1.279|0.391|3.807|1.279|25.044|
......
Total line number = 96
It costs 0.119s
IoTDB:etth> SELECT * FROM forecast(
model_id => 'sundial',
targets => (SELECT Time, ot FROM etth.eg WHERE time >= 2016-08-07T18:00:00.000+08:00 LIMIT 1440) ORDER BY time,
output_length => 96
)
+-----------------------------+---------+
| time| ot|
+-----------------------------+---------+
|2016-10-06T18:00:00.000+08:00|20.781654|
|2016-10-06T19:00:00.000+08:00|20.252121|
|2016-10-06T20:00:00.000+08:00|19.960138|
|2016-10-06T21:00:00.000+08:00|19.662334|
......
Total line number = 96
It costs 1.615s4.2 Registering Custom Models
Transformers models meeting the following criteria can be registered to AINode:
- AINode uses Transformers v4.56.2; avoid inheriting interfaces from older versions (<4.50).
- The model must inherit an AINode inference pipeline class (currently supports forecasting pipeline):
# iotdb-core/ainode/iotdb/ainode/core/inference/pipeline/basic_pipeline.py class BasicPipeline(ABC): def __init__(self, model_id, **model_kwargs): self.model_info = model_info self.device = model_kwargs.get("device", "cpu") self.model = load_model(model_info, device_map=self.device, **model_kwargs) @abstractmethod def preprocess(self, inputs, **infer_kwargs): """Preprocess input data before inference, including shape validation and numerical conversion.""" pass @abstractmethod def postprocess(self, output, **infer_kwargs): """Postprocess model outputs after inference.""" pass class ForecastPipeline(BasicPipeline): def __init__(self, model_info, **model_kwargs): super().__init__(model_info, model_kwargs=model_kwargs) def preprocess(self, inputs: list[dict[str, dict[str, torch.Tensor] | torch.Tensor]], **infer_kwargs): """ Preprocess and validate input data before model inference. Args: inputs (list[dict]): Input data as list of dicts containing: - 'targets': Tensor of shape (input_length,) or (target_count, input_length). - 'past_covariates': Optional dict of tensors, each of shape (input_length,). - 'future_covariates': Optional dict of tensors, each of shape (input_length,). infer_kwargs (dict, optional): Additional inference parameters, e.g.: - `output_length` (int): Required if 'future_covariates' provided for validation. Raises: ValueError: For invalid input formats (missing keys, invalid tensor shapes). Returns: Preprocessed and validated input ready for model inference. """ pass def forecast(self, inputs, **infer_kwargs): """ Perform forecasting on given inputs. Parameters: inputs: Input data for forecasting (type/structure model-specific). **infer_kwargs: Additional parameters, e.g.: - `output_length` (int): Number of future time points to generate. Returns: Forecast output (format model-specific). """ pass def postprocess(self, outputs: list[torch.Tensor], **infer_kwargs) -> list[torch.Tensor]: """ Postprocess model outputs, validate shapes, and ensure expected dimensions. Args: outputs: List of 2D tensors, each of shape `[target_count, output_length]`. Raises: InferenceModelInternalException: For invalid output tensor shapes. ValueError: For incorrect output format. Returns: List of postprocessed 2D tensors. """ pass - Modify
config.jsonto include:{ "auto_map": { "AutoConfig": "config.Chronos2CoreConfig", "AutoModelForCausalLM": "model.Chronos2Model" }, "pipeline_cls": "pipeline_chronos2.Chronos2Pipeline", "model_type": "custom_t5" }- Must specify model Config and model classes via
auto_map. - Must implement and specify the inference pipeline class.
model_typeserves as a unique identifier. Must not conflict with existing model types (for bothbuiltinanduser_definedmodels).
- Must specify model Config and model classes via
- Ensure the model directory contains:
config.json(model configuration)model.safetensors(model weights)- Other
.pyfiles (model code) - Note: Filenames for config and weights are fixed and non-customizable.
SQL Syntax for Registration:
CREATE MODEL <model_id> USING URI <uri>Parameter Details:
- model_id: Unique identifier for the custom model (case-sensitive):
- Allowed characters:
[0-9a-zA-Z_](alphanumeric and underscore; cannot start with digit/underscore) - Length: 2–64 characters
- Allowed characters:
- uri: Local URI path containing model code and weights.
Registration Example:
Upload a custom Transformers model from local path. AINode copies the folder to the user_defined directory.
CREATE MODEL chronos2 USING URI 'file:///path/to/chronos2'Registration proceeds asynchronously. Check status via SHOW MODELS (see Section 4.3). After successful registration, invoke inference via standard queries.
4.3 Viewing Models
Registered models can be queried using:
SHOW MODELSFilter by specific model:
SHOW MODELS <model_id> -- Display specific model onlyResult columns:
| ModelId | ModelType | Category | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model ID | Model Type | Category | State |
State transition diagram:
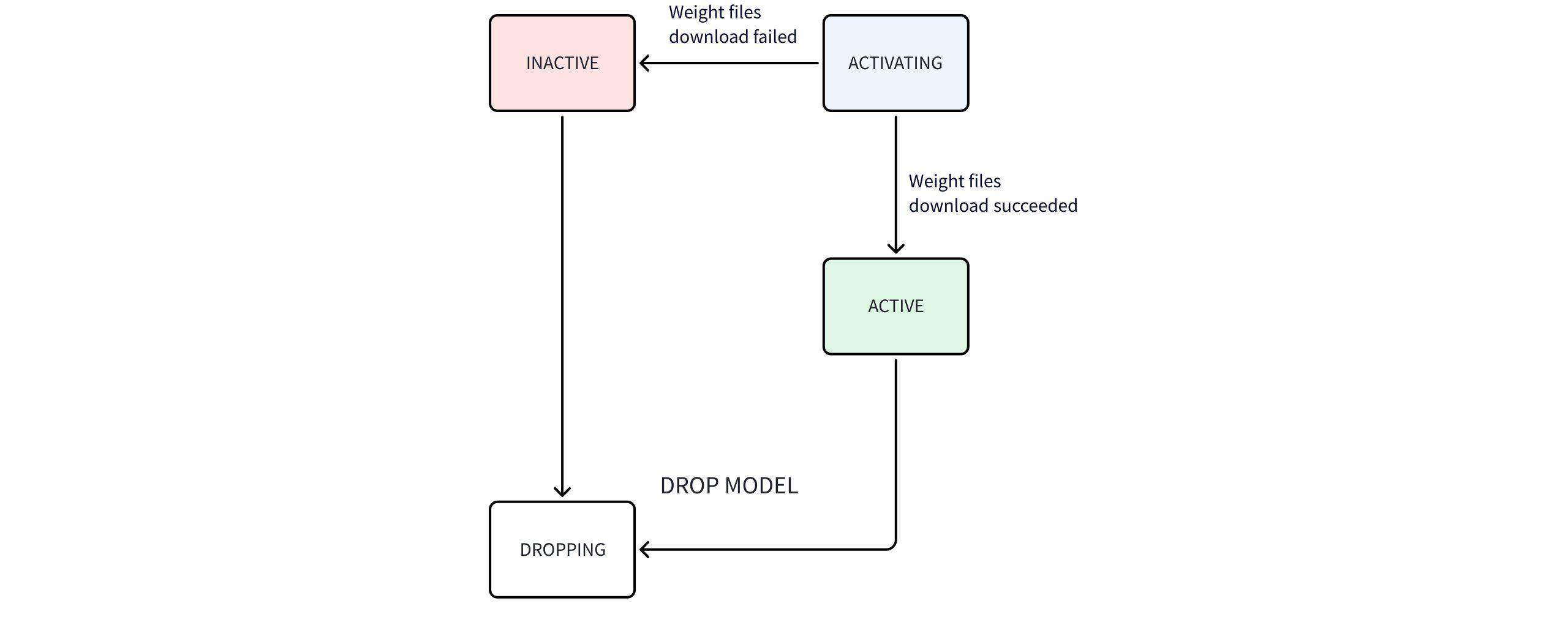
State Flow Explanation:
- After AINode startup,
SHOW MODELSdisplays only system built-in (BUILTIN) models. - User-uploaded models are marked as user-defined (USER_DEFINED). AINode attempts to parse
ModelTypefrom config; displays empty if parsing fails. - Time series large model weights (built-in) are not bundled with AINode. Download occurs on startup:
ACTIVATINGduring download →ACTIVEon success →INACTIVEon failure.
Viewing Example:
IoTDB> SHOW MODELS
+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
| ModelId| ModelType| Category| State|
+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
| arima| sktime| builtin| active|
| holtwinters| sktime| builtin| active|
|exponential_smoothing| sktime| builtin| active|
| naive_forecaster| sktime| builtin| active|
| stl_forecaster| sktime| builtin| active|
| gaussian_hmm| sktime| builtin| active|
| gmm_hmm| sktime| builtin| active|
| stray| sktime| builtin| active|
| custom| | user_defined| active|
| timer_xl| timer| builtin| activating|
| sundial| sundial| builtin| active|
| chronos2| t5| builtin| inactive|
+---------------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+Built-in Traditional Time Series Models:
| Model Name | Core Concept | Applicable Scenarios | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) | Combines AR, differencing (I), and MA for stationary or differenced series | Univariate forecasting (stock prices, sales, economics) | 1. For linear trends with weak seasonality2. Requires (p,d,q) tuning3. Sensitive to missing values |
| Holt-Winters (Triple Exponential Smoothing) | Exponential smoothing with level, trend, and seasonal components | Data with clear trend & seasonality (monthly sales, power demand) | 1. Handles additive/multiplicative seasonality2. Weights recent data higher3. Simple implementation |
| Exponential Smoothing | Weighted average of history with exponentially decaying weights | Trending but non-seasonal data (short-term demand) | 1. Few parameters, simple computation2. Suitable for stable/slow-changing series3. Extensible to double/triple smoothing |
| Naive Forecaster | Uses last observation as next prediction (simplest baseline) | Benchmarking or data with no clear pattern | 1. No training needed2. Sensitive to sudden changes3. Seasonal variant uses prior season value |
| STL Forecaster | Decomposes series into trend, seasonal, residual; forecasts components | Complex seasonality/trends (climate, traffic) | 1. Handles non-fixed seasonality2. Robust to outliers3. Components can use other models |
| Gaussian HMM | Hidden states generate observations; each state follows Gaussian distribution | State sequence prediction/classification (speech, finance) | 1. Models temporal state transitions2. Observations independent per state3. Requires state count |
| GMM HMM | Extends Gaussian HMM; each state uses Gaussian Mixture Model | Multi-modal observation scenarios (motion recognition, biosignals) | 1. More flexible than single Gaussian2. Higher complexity3. Requires GMM component count |
| STRAY (Search for Outliers using Random Projection and Adaptive Thresholding) | Uses SVD to detect anomalies in high-dimensional time series | High-dimensional anomaly detection (sensor networks, IT monitoring) | 1. No distribution assumption2. Handles high dimensions3. Sensitive to global anomalies |
Built-in Time Series Large Models:
| Model Name | Core Concept | Applicable Scenarios | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timer-XL | Long-context time series large model pretrained on massive industrial data | Complex industrial forecasting requiring ultra-long history (energy, aerospace, transport) | 1. Supports input of tens of thousands of time points2. Covers non-stationary, multivariate, and covariate scenarios3. Pretrained on trillion-scale high-quality industrial IoT data |
| Timer-Sundial | Generative foundation model with "Transformer + TimeFlow" architecture | Zero-shot forecasting requiring uncertainty quantification (finance, supply chain, renewable energy) | 1. Strong zero-shot generalization; supports point & probabilistic forecasting2. Flexible analysis of any prediction distribution statistic3. Innovative flow-matching architecture for efficient non-deterministic sample generation |
| Chronos-2 | Universal time series foundation model based on discrete tokenization | Rapid zero-shot univariate forecasting; scenarios enhanced by covariates (promotions, weather) | 1. Powerful zero-shot probabilistic forecasting2. Unified multi-variable & covariate modeling (strict input requirements): a. Future covariate names ⊆ historical covariate names b. Each historical covariate length = target length c. Each future covariate length = prediction length3. Efficient encoder-only structure balancing performance and speed |
4.4 Deleting Models
Registered models can be deleted via SQL. AINode removes the corresponding folder under user_defined. Syntax:
DROP MODEL <model_id>- Specify a successfully registered
model_id. - Deletion is asynchronous; model enters
DROPPINGstate (unavailable for inference during this phase). - Built-in models cannot be deleted.
4.5 Loading/Unloading Models
AINode supports two loading strategies:
- On-Demand Loading: Load model temporarily during inference, then release resources. Suitable for testing or low-load scenarios.
- Persistent Loading: Keep model instances resident in CPU memory or GPU VRAM to support high-concurrency inference. Users specify load/unload targets via SQL; AINode auto-manages instance counts. Current loaded status is queryable.
Details below:
Configuration Parameters
Edit these settings to control persistent loading behavior:# Ratio of total device memory/VRAM usable by AINode for inference # Datatype: Float ain_inference_memory_usage_ratio=0.4 # Memory overhead ratio per loaded model instance (model_size * this_value) # Datatype: Float ain_inference_extra_memory_ratio=1.2List Available Devices
SHOW AI_DEVICESExample:
IoTDB> SHOW AI_DEVICES +-------------+ | DeviceId| +-------------+ | cpu| | 0| | 1| +-------------+Load Model
Manually load model; system auto-balances instance count based on resources:LOAD MODEL <existing_model_id> TO DEVICES <device_id>(, <device_id>)*Parameters:
existing_model_id: Model ID (current version supportstimer_xlandsundialonly)device_id:cpu: Load into server memorygpu_id: Load into specified GPU(s), e.g.,'0,1'for GPUs 0 and 1
Example:
LOAD MODEL sundial TO DEVICES 'cpu,0,1'Unload Model
Unload all instances of a model; system reallocates freed resources:UNLOAD MODEL <existing_model_id> FROM DEVICES <device_id>(, <device_id>)*Parameters same as
LOAD MODEL.
Example:UNLOAD MODEL sundial FROM DEVICES 'cpu,0,1'View Loaded Models
SHOW LOADED MODELS SHOW LOADED MODELS <device_id>(, <device_id>)* -- Filter by deviceExample (sundial loaded on CPU, GPU 0, GPU 1):
IoTDB> SHOW LOADED MODELS +-------------+--------------+------------------+ | DeviceId| ModelId| Count(instances)| +-------------+--------------+------------------+ | cpu| sundial| 4| | 0| sundial| 6| | 1| sundial| 6| +-------------+--------------+------------------+DeviceId: Device identifierModelId: Loaded model IDCount(instances): Number of model instances per device (auto-assigned by system)
4.6 Time Series Large Models Overview
AINode supports multiple time series large models. For detailed introduction and deployment guidance, refer to Time Series Large Models.
5. Permission Management
AINode leverages IoTDB's native authentication system. Users require USE_MODEL permission to manage models. For inference, users must have access permissions to source time series referenced in the input SQL.
| Permission Name | Scope | Admin User (default ROOT) | Regular User |
|---|---|---|---|
| USE_MODEL | CREATE MODEL / SHOW MODELS / DROP MODEL | √ | √ |
| READ_SCHEMA & READ_DATA | FORECAST | √ | √ |
6. Contributing Open Source Time Series Large Models to IoTDB-AINode
To add a new built-in custom model to AINode (using Chronos2 as example):
Initiate Discussion
Email dev@iotdb.apache.org or open an issue in the main repository.Submit Pull Request to Main Branch
- Verify the model's open-source license and declare it appropriately in the IoTDB repository.
- Create a new package for the model under
iotdb-core/ainode/iotdb/ainode/core/model/:- Include model configuration class
- Include model class for inference execution
- Include class inheriting AINode's inference pipeline
root@rootMacBook-Pro model % eza --tree --level=2 . . ├── chronos2 │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── base.py │ ├── chronos_bolt.py │ ├── config.py │ ├── dataset.py │ ├── layers.py │ ├── model.py │ ├── pipeline_chronos2.py # Inherits AINode inference pipeline │ └── utils.py ├── sktime ├── sundial └── timer_xl - Add model metadata in
iotdb-core/ainode/iotdb/ainode/core/model/model_info.py:BUILTIN_HF_TRANSFORMERS_MODEL_MAP = { "chronos2": ModelInfo( model_id="chronos2", category=ModelCategory.BUILTIN, state=ModelStates.INACTIVE, model_type="t5", pipeline_cls="pipeline_chronos2.Chronos2Pipeline", repo_id="amazon/chronos-2", # [Optional] HuggingFace weights repo auto_map={ "AutoConfig": "config.Chronos2CoreConfig", "AutoModelForCausalLM": "model.Chronos2Model", }, ), } - Add model entry in
integration-test/src/test/java/org/apache/iotdb/ainode/utils/AINodeTestUtils.java:public static final Map<String, FakeModelInfo> BUILTIN_LTSM_MAP = Stream.of( new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>( "sundial", new FakeModelInfo("sundial", "sundial", "builtin", "active")), new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>( "timer_xl", new FakeModelInfo("timer_xl", "timer", "builtin", "active")), new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>( "chronos2", new FakeModelInfo("chronos2", "t5", "builtin", "active"))) .collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue)); - Submit PR; ensure CI tests pass before merging.
Packaging and Deployment
- Build AINode to generate installation package:
# Build IoTDB and AINode together mvn clean package -pl distribution -P with-ainode -am -DskipTests # Build AINode only mvn clean package -pl iotdb-core/ainode -P with-ainode -am -DskipTests - Ensure model weights are accessible at runtime:
- If weights are fetchable from HuggingFace, confirm
repo_idis set. - Otherwise, manually place weights in
data/ainode/models/builtin/<model_id>before/during startup.
root@rootMacBook-Pro models % eza --tree --level=3 . . ├── __init__.py ├── builtin │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── chronos2 │ │ ├── __init__.py │ │ ├── config.json │ │ └── model.safetensors │ ├── sundial │ │ ├── __init__.py │ │ ├── config.json │ │ └── model.safetensors │ └── timer_xl │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── config.json │ └── model.safetensors └── user_defined - If weights are fetchable from HuggingFace, confirm
- Build AINode to generate installation package:
Complete Example
Reference implementation: https://github.com/apache/iotdb/pull/16903
