Cluster Deployment
Cluster Deployment
This section will take the IoTDB classic cluster deployment architecture 3C3D (3 ConfigNodes and 3 DataNodes) as an example to introduce how to deploy a cluster, commonly known as the 3C3D cluster. The architecture diagram of the 3C3D cluster is as follows:
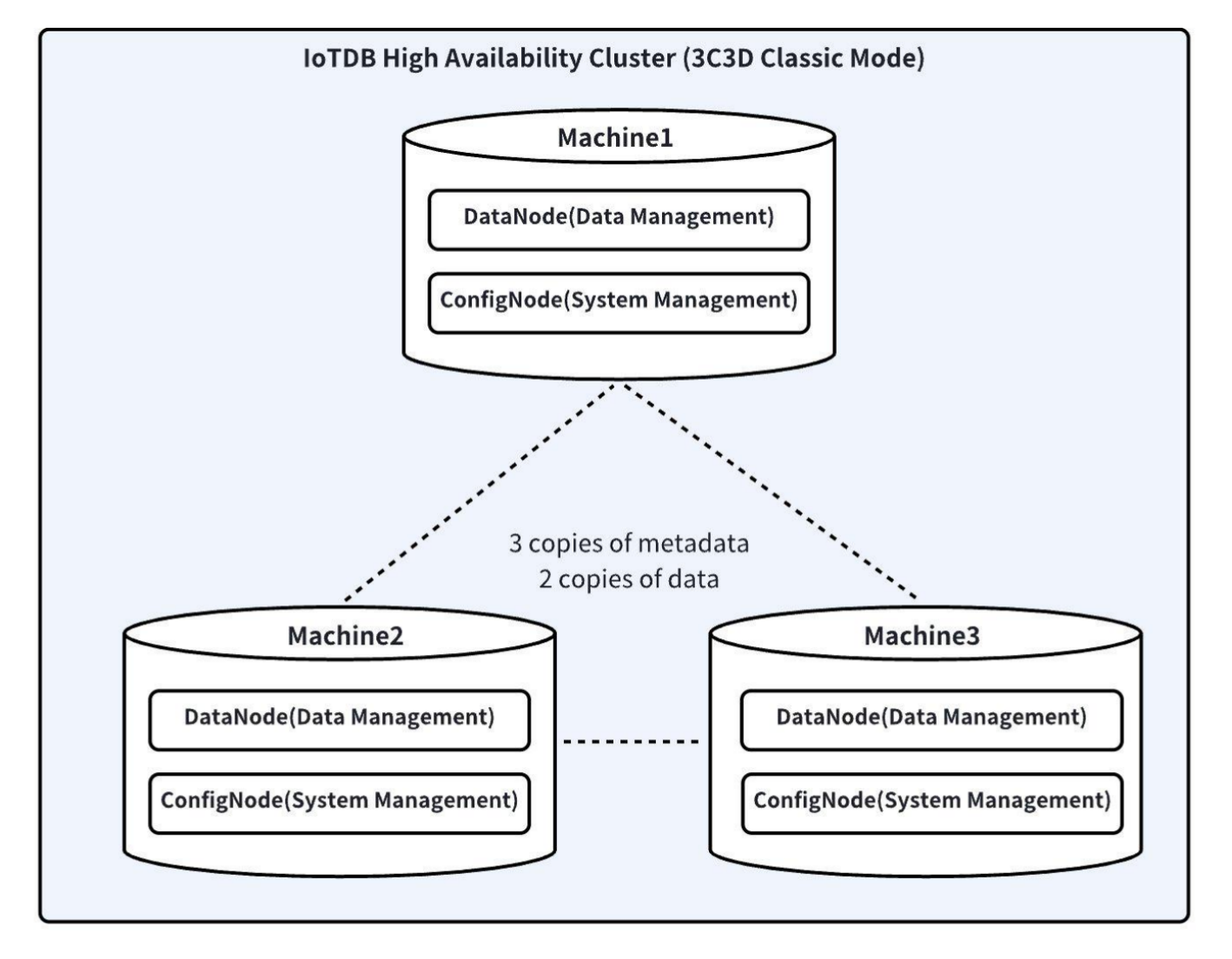
1. Note
Before installation, ensure that the system is complete by referring to System configuration
It is recommended to prioritize using
hostnamefor IP configuration during deployment, which can avoid the problem of modifying the host IP in the later stage and causing the database to fail to start. To set the host name, you need to configure /etc/hosts on the target server. For example, if the local IP is 192.168.1.3 and the host name is iotdb-1, you can use the following command to set the server's host name and configure thecn_internal_addressanddn_internal_addressof IoTDB using the host name.echo "192.168.1.3 iotdb-1" >> /etc/hostsSome parameters cannot be modified after the first startup. Please refer to the "Parameter Configuration" section below for settings.
Whether in linux or windows, ensure that the IoTDB installation path does not contain Spaces and Chinese characters to avoid software exceptions.
Please note that when installing and deploying IoTDB, it is necessary to use the same user for operations. You can:
- Using root user (recommended): Using root user can avoid issues such as permissions.
- Using a fixed non root user:
- Using the same user operation: Ensure that the same user is used for start, stop and other operations, and do not switch users.
- Avoid using sudo: Try to avoid using sudo commands as they execute commands with root privileges, which may cause confusion or security issues.
- Before installation, the health check tool can help inspect the operating environment of IoTDB nodes and obtain detailed inspection results. The usage method of the IoTDB health check tool can be found in:Health Check Tool.
2. Preparation Steps
Prepare the IoTDB database installation package::apache-iotdb-{version}-all-bin.zip(Please refer to the installation package for details:IoTDB-Package)
Configure the operating system environment according to environmental requirements (system environment configuration can be found in:Environment Requirement)
2.1 Pre-installation Check
To ensure the IoTDB installation package you obtained is complete and valid, we recommend performing an SHA512 verification before proceeding with the installation and deployment.
Preparation:
- Obtain the officially released SHA512 checksum: Visit the Release Versions page on the IoTDB open-source official website to get it.
Verification Steps (Linux as an Example):
- Open the terminal and navigate to the directory where the installation package is stored (e.g., /data/iotdb):
cd /data/iotdb - Execute the following command to calculate the hash value:
sha512sum apache-iotdb-{version}-all-bin.zip - The terminal will output a result (the left part is the SHA512 checksum, and the right part is the file name):
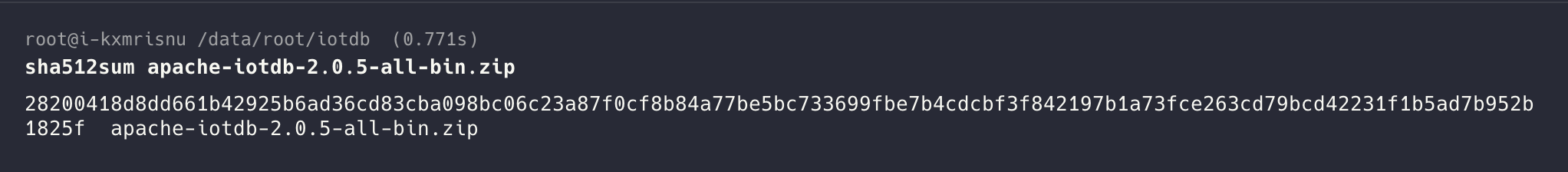
- Compare the output result with the official SHA512 checksum. Once confirmed that they match, you can proceed with the installation and deployment of IoTDB as per the procedures below.
Notes:
- If the verification results do not match, please re-obtain the installation package.
- If a "file not found" prompt appears during verification, check whether the file path is correct or if the installation package has been fully downloaded.
3. Installation Steps
Assuming there are three Linux servers now, the IP addresses and service roles are assigned as follows:
| Node IP | Host Name | Service |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.3 | iotdb-1 | ConfigNode、DataNode |
| 192.168.1.4 | iotdb-2 | ConfigNode、DataNode |
| 192.168.1.5 | iotdb-3 | ConfigNode、DataNode |
3.1 Set Host Name
On three machines, configure the host names separately. To set the host names, configure /etc/hosts on the target server. Use the following command:
echo "192.168.1.3 iotdb-1" >> /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.1.4 iotdb-2" >> /etc/hosts
echo "192.168.1.5 iotdb-3" >> /etc/hosts3.2 Configuration
Unzip the installation package and enter the installation directory
unzip apache-iotdb-{version}-all-bin.zip
cd apache-iotdb-{version}-all-binEnvironment Script Configuration
./conf/confignode-env.shconfiguration
| 配置项 | Description | Default | Recommended value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMORY_SIZE | The total amount of memory that IoTDB ConfigNode nodes can use | - | Can be filled in as needed, and the system will allocate memory based on the filled in values | Save changes without immediate execution; modifications take effect after service restart. |
./conf/datanode-env.shconfiguration
| Configuration | Description | Default | Recommended value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMORY_SIZE | The total amount of memory that IoTDB DataNode nodes can use | - | Can be filled in as needed, and the system will allocate memory based on the filled in values | Save changes without immediate execution; modifications take effect after service restart. |
General Configuration
Open the general configuration file ./conf/iotdb-system.properties, The following parameters can be set according to the deployment method:
| Configuration | Description | 192.168.1.3 | 192.168.1.4 | 192.168.1.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cluster_name | Cluster Name | defaultCluster | defaultCluster | defaultCluster |
| schema_replication_factor | The number of metadata replicas, the number of DataNodes should not be less than this number | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| data_replication_factor | The number of data replicas should not be less than this number of DataNodes | 2 | 2 | 2 |
ConfigNode Configuration
Open the ConfigNode configuration file ./conf/iotdb-system.properties, Set the following parameters
| Configuration | Description | Default | Recommended value | 192.168.1.3 | 192.168.1.4 | 192.168.1.5 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cn_internal_address | The address used by ConfigNode for communication within the cluster | 127.0.0.1 | The IPV4 address or host name of the server where it is located, and it is recommended to use host name | iotdb-1 | iotdb-2 | iotdb-3 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| cn_internal_port | The port used by ConfigNode for communication within the cluster | 10710 | 10710 | 10710 | 10710 | 10710 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| cn_consensus_port | The port used for ConfigNode replica group consensus protocol communication | 10720 | 10720 | 10720 | 10720 | 10720 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| cn_seed_config_node | The address of the ConfigNode that the node connects to when registering to join the cluster, cn_internal_address:cn_internal_port | 127.0.0.1:10710 | The first CongfigNode's cn_internal-address: cn_internal_port | iotdb-1:10710 | iotdb-1:10710 | iotdb-1:10710 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
DataNode Configuration
Open DataNode Configuration File ./conf/iotdb-system.properties,Set the following parameters:
| Configuration | Description | Default | Recommended value | 192.168.1.3 | 192.168.1.4 | 192.168.1.5 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dn_rpc_address | The address of the client RPC service | 127.0.0.1 | By default, the local machine can directly access it. For non-local access, please modify this configuration item to the IPv4 address or hostname of the server where it is located. It is recommended to use the IPv4 address of the server where it is located. | iotdb-1 | iotdb-2 | iotdb-3 | Restarting the service takes effect |
| dn_rpc_port | The port of the client RPC service | 6667 | 6667 | 6667 | 6667 | 6667 | Restarting the service takes effect |
| dn_internal_address | The address used by DataNode for communication within the cluster | 127.0.0.1 | The IPV4 address or host name of the server where it is located, and it is recommended to use host name | iotdb-1 | iotdb-2 | iotdb-3 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| dn_internal_port | The port used by DataNode for communication within the cluster | 10730 | 10730 | 10730 | 10730 | 10730 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| dn_mpp_data_exchange_port | The port used by DataNode to receive data streams | 10740 | 10740 | 10740 | 10740 | 10740 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| dn_data_region_consensus_port | The port used by DataNode for data replica consensus protocol communication | 10750 | 10750 | 10750 | 10750 | 10750 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| dn_schema_region_consensus_port | The port used by DataNode for metadata replica consensus protocol communication | 10760 | 10760 | 10760 | 10760 | 10760 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
| dn_seed_config_node | The address of the ConfigNode that the node connects to when registering to join the cluster, i.e. cn_internal-address: cn_internal_port | 127.0.0.1:10710 | The first CongfigNode's cn_internal-address: cn_internal_port | iotdb-1:10710 | iotdb-1:10710 | iotdb-1:10710 | Cannot be modified after initial startup |
❗️Attention: Editors such as VSCode Remote do not have automatic configuration saving function. Please ensure that the modified files are saved persistently, otherwise the configuration items will not take effect
3.3 Start ConfigNode
Start the first confignode of IoTDB-1 first, ensuring that the seed confignode node starts first, and then start the second and third confignode nodes in sequence
cd sbin
./start-confignode.sh -d #"- d" parameter will start in the backgroundIf the startup fails, please refer to Common Questions.
3.4 Start DataNode
Enter the sbin directory of iotdb and start three datanode nodes in sequence:
cd sbin
./start-datanode.sh -d #"- d" parameter will start in the background3.5 Verify Deployment
Can be executed directly Cli startup script in ./sbin directory:
./start-cli.sh -h ip(local IP or domain name) -p port(6667)After successful startup, the following interface will appear displaying successful installation of IOTDB.
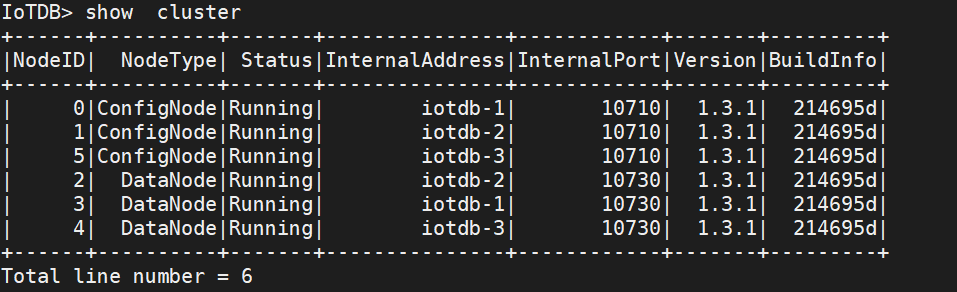
You can use the show cluster command to view cluster information:
The appearance of
ACTIVATED (W)indicates passive activation, which means that this Configurable Node does not have a license file (or has not issued the latest license file with a timestamp), and its activation depends on other Activated Configurable Nodes in the cluster. At this point, it is recommended to check if the license file has been placed in the license folder. If not, please place the license file. If a license file already exists, it may be due to inconsistency between the license file of this node and the information of other nodes. Please contact Timecho staff to reapply.
3.6 One-click Cluster Start and Stop
3.6.1 Overview
Within the root directory of IoTDB, the sbin subdirectory houses the start-all.sh and stop-all.sh scripts, which work in concert with the iotdb-cluster.properties configuration file located in the conf subdirectory. This synergy enables the one-click initiation or termination of all nodes within the cluster from a single node. This approach facilitates efficient management of the IoTDB cluster's lifecycle, streamlining the deployment and operational maintenance processes.
This following section will introduce the specific configuration items in the iotdb-cluster.properties file.
3.6.2 Configuration Items
Note:
- When the cluster changes, this configuration file needs to be manually updated.
- If the
iotdb-cluster.propertiesconfiguration file is not set up and thestart-all.shorstop-all.shscripts are executed, the scripts will, by default, start or stop the ConfigNode and DataNode nodes located in the IOTDB_HOME directory where the scripts reside.- It is recommended to configure SSH passwordless login: If not configured, the script will prompt for the server password after execution to facilitate subsequent start, stop, or destroy operations. If already configured, there is no need to enter the server password during script execution.
- confignode_address_list
| Name | confignode_address_list |
|---|---|
| Description | A list of IP addresses of the hosts where the ConfigNodes to be started/stopped are located. If there are multiple, they should be separated by commas. |
| Type | String |
| Default | None |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
- datanode_address_list
| Name | datanode_address_list |
|---|---|
| Description | A list of IP addresses of the hosts where the DataNodes to be started/stopped are located. If there are multiple, they should be separated by commas. |
| Type | String |
| Default | None |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
- ssh_account
| Name | ssh_account |
|---|---|
| Description | The username used to log in to the target hosts via SSH. All hosts must have the same username. |
| Type | String |
| Default | root |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
- ssh_port
| Name | ssh_port |
|---|---|
| Description | The SSH port exposed by the target hosts. All hosts must have the same SSH port. |
| Type | int |
| Default | 22 |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
- confignode_deploy_path
| Name | confignode_deploy_path |
|---|---|
| Description | The path on the target hosts where all ConfigNodes to be started/stopped are located. All ConfigNodes must be in the same directory on their respective hosts. |
| Type | String |
| Default | None |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
- datanode_deploy_path
| Name | datanode_deploy_path |
|---|---|
| Description | The path on the target hosts where all DataNodes to be started/stopped are located. All DataNodes must be in the same directory on their respective hosts. |
| Type | String |
| Default | None |
| Effective | After restarting the system |
4. Node Maintenance Steps
4.1 ConfigNode Node Maintenance
ConfigNode node maintenance is divided into two types of operations: adding and removing ConfigNodes, with two common use cases:
- Cluster expansion: For example, when there is only one ConfigNode in the cluster, and you want to increase the high availability of ConfigNode nodes, you can add two ConfigNodes, making a total of three ConfigNodes in the cluster.
- Cluster failure recovery: When the machine where a ConfigNode is located fails, making the ConfigNode unable to run normally, you can remove this ConfigNode and then add a new ConfigNode to the cluster.
❗️Note, after completing ConfigNode node maintenance, you need to ensure that there are 1 or 3 ConfigNodes running normally in the cluster. Two ConfigNodes do not have high availability, and more than three ConfigNodes will lead to performance loss.
Adding ConfigNode Nodes
Script command:
# Linux / MacOS
# First switch to the IoTDB root directory
sbin/start-confignode.sh
# Windows
# First switch to the IoTDB root directory
# Before version V2.0.4.x
sbin\start-confignode.bat
# V2.0.4.x and later versions
sbin\windows\start-confignode.batParameter introduction:
| Parameter | Description | Is it required |
|---|---|---|
| -v | Show version information | No |
| -f | Run the script in the foreground, do not put it in the background | No |
| -d | Start in daemon mode, i.e. run in the background | No |
| -p | Specify a file to store the process ID for process management | No |
| -c | Specify the path to the configuration file folder, the script will load the configuration file from here | No |
| -g | Print detailed garbage collection (GC) information | No |
| -H | Specify the path of the Java heap dump file, used when JVM memory overflows | No |
| -E | Specify the path of the JVM error log file | No |
| -D | Define system properties, in the format key=value | No |
| -X | Pass -XX parameters directly to the JVM | No |
| -h | Help instruction | No |
Removing ConfigNode Nodes
First connect to the cluster through the CLI and confirm the internal address and port number of the ConfigNode you want to remove by using show confignodes:
IoTDB> show confignodes
+------+-------+---------------+------------+--------+
|NodeID| Status|InternalAddress|InternalPort| Role|
+------+-------+---------------+------------+--------+
| 0|Running| 127.0.0.1| 10710| Leader|
| 1|Running| 127.0.0.1| 10711|Follower|
| 2|Running| 127.0.0.1| 10712|Follower|
+------+-------+---------------+------------+--------+
Total line number = 3
It costs 0.030sThen use the script to remove the ConfigNode. Script command:
# Linux / MacOS
sbin/remove-confignode.sh [confignode_id]
#Windows
# Before version V2.0.4.x
sbin\remove-confignode.bat [confignode_id]
# V2.0.4.x and later versions
sbin\windows\remove-confignode.bat [confignode_id]4.2 DataNode Node Maintenance
There are two common scenarios for DataNode node maintenance:
- Cluster expansion: For the purpose of expanding cluster capabilities, add new DataNodes to the cluster
- Cluster failure recovery: When a machine where a DataNode is located fails, making the DataNode unable to run normally, you can remove this DataNode and add a new DataNode to the cluster
❗️Note, in order for the cluster to work normally, during the process of DataNode node maintenance and after the maintenance is completed, the total number of DataNodes running normally should not be less than the number of data replicas (usually 2), nor less than the number of metadata replicas (usually 3).
Adding DataNode Nodes
Script command:
# Linux / MacOS
# First switch to the IoTDB root directory
sbin/start-datanode.sh
# Windows
# First switch to the IoTDB root directory
# Before version V2.0.4.x
sbin\start-datanode.bat
# V2.0.4.x and later versions
sbin\windows\start-datanode.batParameter introduction:
| Abbreviation | Description | Is it required |
|---|---|---|
| -v | Show version information | No |
| -f | Run the script in the foreground, do not put it in the background | No |
| -d | Start in daemon mode, i.e. run in the background | No |
| -p | Specify a file to store the process ID for process management | No |
| -c | Specify the path to the configuration file folder, the script will load the configuration file from here | No |
| -g | Print detailed garbage collection (GC) information | No |
| -H | Specify the path of the Java heap dump file, used when JVM memory overflows | No |
| -E | Specify the path of the JVM error log file | No |
| -D | Define system properties, in the format key=value | No |
| -X | Pass -XX parameters directly to the JVM | No |
| -h | Help instruction | No |
Note: After adding a DataNode, as new writes arrive (and old data expires, if TTL is set), the cluster load will gradually balance towards the new DataNode, eventually achieving a balance of storage and computation resources on all nodes.
Removing DataNode Nodes
First connect to the cluster through the CLI and confirm the RPC address and port number of the DataNode you want to remove with show datanodes:
IoTDB> show datanodes
+------+-------+----------+-------+-------------+---------------+
|NodeID| Status|RpcAddress|RpcPort|DataRegionNum|SchemaRegionNum|
+------+-------+----------+-------+-------------+---------------+
| 1|Running| 0.0.0.0| 6667| 0| 0|
| 2|Running| 0.0.0.0| 6668| 1| 1|
| 3|Running| 0.0.0.0| 6669| 1| 0|
+------+-------+----------+-------+-------------+---------------+
Total line number = 3
It costs 0.110sThen use the script to remove the DataNode. Script command:
# Linux / MacOS
sbin/remove-datanode.sh [datanode_id]
#Windows
# Before version V2.0.4.x
sbin\remove-datanode.bat [datanode_id]
# V2.0.4.x and later versions
sbin\windows\remove-datanode.bat [datanode_id]4.3 Cluster Maintenance
For more details on cluster maintenance, please refer to: Cluster Maintenance
5. Questions
Confignode failed to start
Step 1: Please check the startup log to see if any parameters that cannot be changed after the first startup have been modified.
Step 2: Please check the startup log for any other abnormalities. If there are any abnormal phenomena in the log, please contact Timecho Technical Support personnel for consultation on solutions.
Step 3: If it is the first deployment or data can be deleted, you can also clean up the environment according to the following steps, redeploy, and restart.
Step 4: Clean up the environment:
a. Terminate all ConfigNode Node and DataNode processes.
# 1. Stop the ConfigNode and DataNode services sbin/stop-standalone.sh # 2. Check for any remaining processes jps # Or ps -ef|grep iotdb # 3. If there are any remaining processes, manually kill the kill -9 <pid> # If you are sure there is only one iotdb on the machine, you can use the following command to clean up residual processes ps -ef|grep iotdb|grep -v grep|tr -s ' ' ' ' |cut -d ' ' -f2|xargs kill -9b. Delete the data and logs directories.
Explanation: Deleting the data directory is necessary, deleting the logs directory is for clean logs and is not mandatory.
cd /data/iotdb rm -rf data logs
