Command Line Interface(CLI)
Command Line Interface(CLI)
IoTDB provides Cli/shell tools for users to interact with IoTDB server in command lines. This document shows how Cli/shell tool works and the meaning of its parameters.
Note: In this document, $IOTDB_HOME represents the path of the IoTDB installation directory.
Installation
Under the root path of iotdb:
> mvn clean package -pl cli -am -DskipTestsAfter build, the IoTDB cli will be in the folder "cli/target/iotdb-cli-{project.version}".
Running
Running Cli
After installation, there is a default user in IoTDB: root, and the
default password is root. Users can use this username to try IoTDB Cli/Shell tool. The cli startup script is the start-cli file under the $IOTDB_HOME/bin folder. When starting the script, you need to specify the IP and PORT. (Make sure the IoTDB server is running properly when you use Cli/Shell tool to connect it.)
Here is an example where the server is started locally and the user has not changed the running port. The default rpc port is
6667
If you need to connect to the remote server or changes
the rpc port number of the server running, set the specific IP and RPC PORT at -h and -p.
You also can set your own environment variable at the front of the start script ("/sbin/start-cli.sh" for linux and "/sbin/start-cli.bat" for windows)
The Linux and MacOS system startup commands are as follows:
Shell > sbin/start-cli.sh -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6667 -u root -pw rootThe Windows system startup commands are as follows:
Shell > sbin\start-cli.bat -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6667 -u root -pw rootAfter using these commands, the cli can be started successfully. The successful status will be as follows:
_____ _________ ______ ______
|_ _| | _ _ ||_ _ `.|_ _ \
| | .--.|_/ | | \_| | | `. \ | |_) |
| | / .'`\ \ | | | | | | | __'.
_| |_| \__. | _| |_ _| |_.' /_| |__) |
|_____|'.__.' |_____| |______.'|_______/ version <version>
IoTDB> login successfully
IoTDB>Enter quit or exit can exit Cli. The cli will shows quit normally
Cli Parameters
| Parameter name | Parameter type | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -disableISO8601 | No parameters | No | If this parameter is set, IoTDB will print the timestamp in digital form | -disableISO8601 |
-h <host> | string, no quotation marks | Yes | The IP address of the IoTDB server | -h 10.129.187.21 |
| -help | No parameters | No | Print help information for IoTDB | -help |
-p <rpcPort> | int | Yes | The rpc port number of the IoTDB server. IoTDB runs on rpc port 6667 by default | -p 6667 |
-pw <password> | string, no quotation marks | No | The password used for IoTDB to connect to the server. If no password is entered, IoTDB will ask for password in Cli command | -pw root |
-u <username> | string, no quotation marks | Yes | User name used for IoTDB to connect the server | -u root |
-maxPRC <maxPrintRowCount> | int | No | Set the maximum number of rows that IoTDB returns | -maxPRC 10 |
-e <execute> | string | No | manipulate IoTDB in batches without entering cli input mode | -e "show storage group" |
| -c | empty | No | If the server enables rpc_thrift_compression_enable=true, then cli must use -c | -c |
Following is a cli command which connects the host with IP
10.129.187.21, rpc port 6667, username "root", password "root", and prints the timestamp in digital form. The maximum number of lines displayed on the IoTDB command line is 10.
The Linux and MacOS system startup commands are as follows:
Shell > sbin/start-cli.sh -h 10.129.187.21 -p 6667 -u root -pw root -disableISO8601 -maxPRC 10The Windows system startup commands are as follows:
Shell > sbin\start-cli.bat -h 10.129.187.21 -p 6667 -u root -pw root -disableISO8601 -maxPRC 10Note on using the CLI with OpenID Connect Auth enabled on Server side
Openid connect (oidc) uses keycloack as the authority authentication service of oidc service
configuration
The configuration is located in iotdb-engines.properties , set the author_provider_class is org.apache.iotdb.db.auth.authorizer.OpenIdAuthorizer Openid service is enabled, and the default value is org.apache.iotdb.db.auth.authorizer.LocalFileAuthorizer Indicates that the openid service is not enabled.
authorizer_provider_class=org.apache.iotdb.db.auth.authorizer.OpenIdAuthorizerIf the openid service is turned on, openid_URL is required,openID_url value is http://ip:port/auth/realms/{realmsName}
openID_url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth/realms/iotdb/####keycloack configuration
1、Download the keycloack file and start keycloack in keycloack/bin
Shell >cd bin
Shell >./standalone.sh2、use url(https://ip:port/auth) login keycloack, the first login needs to create a user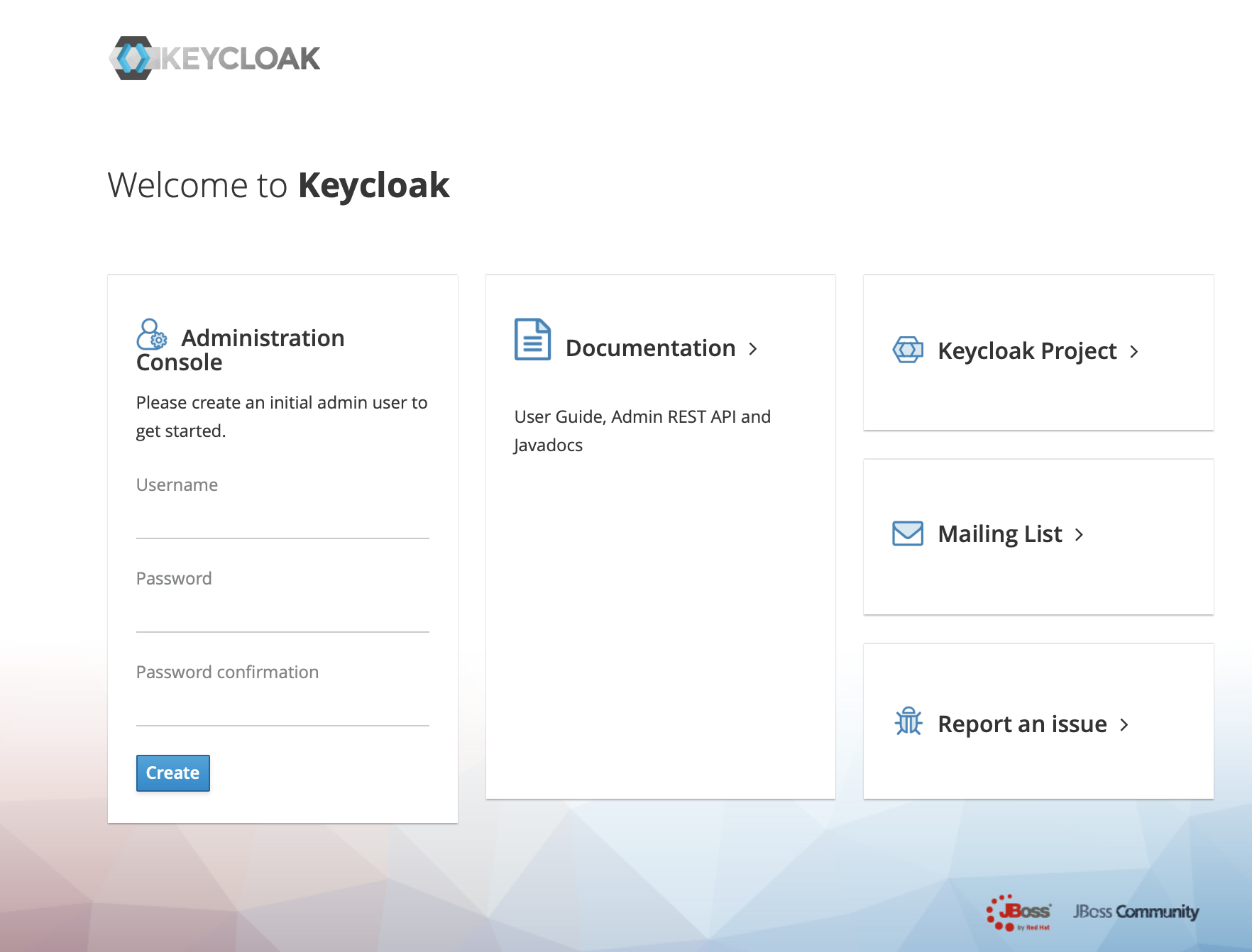
3、Click administration console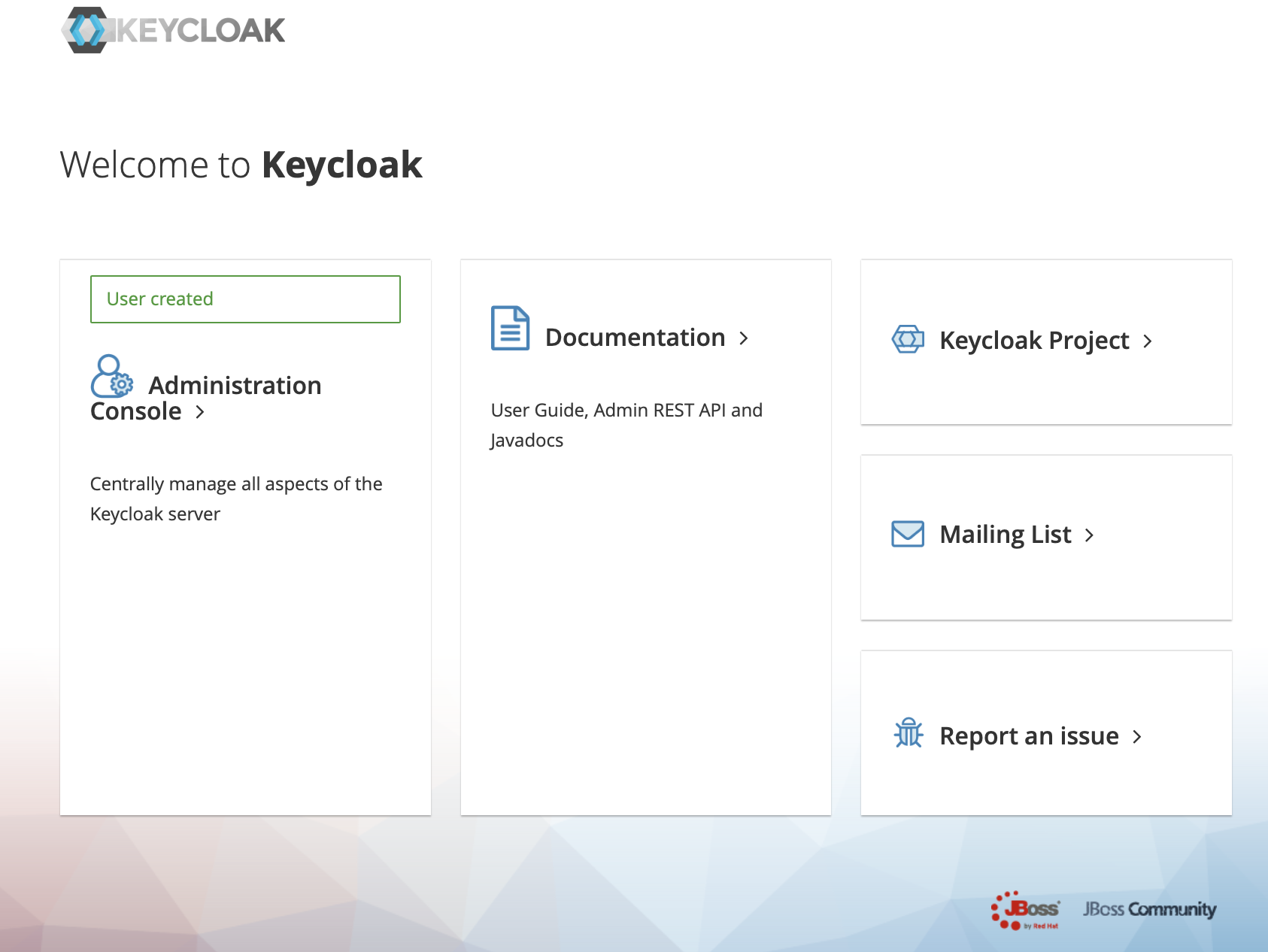
4、In the master menu on the left, click Add realm and enter name to create a new realm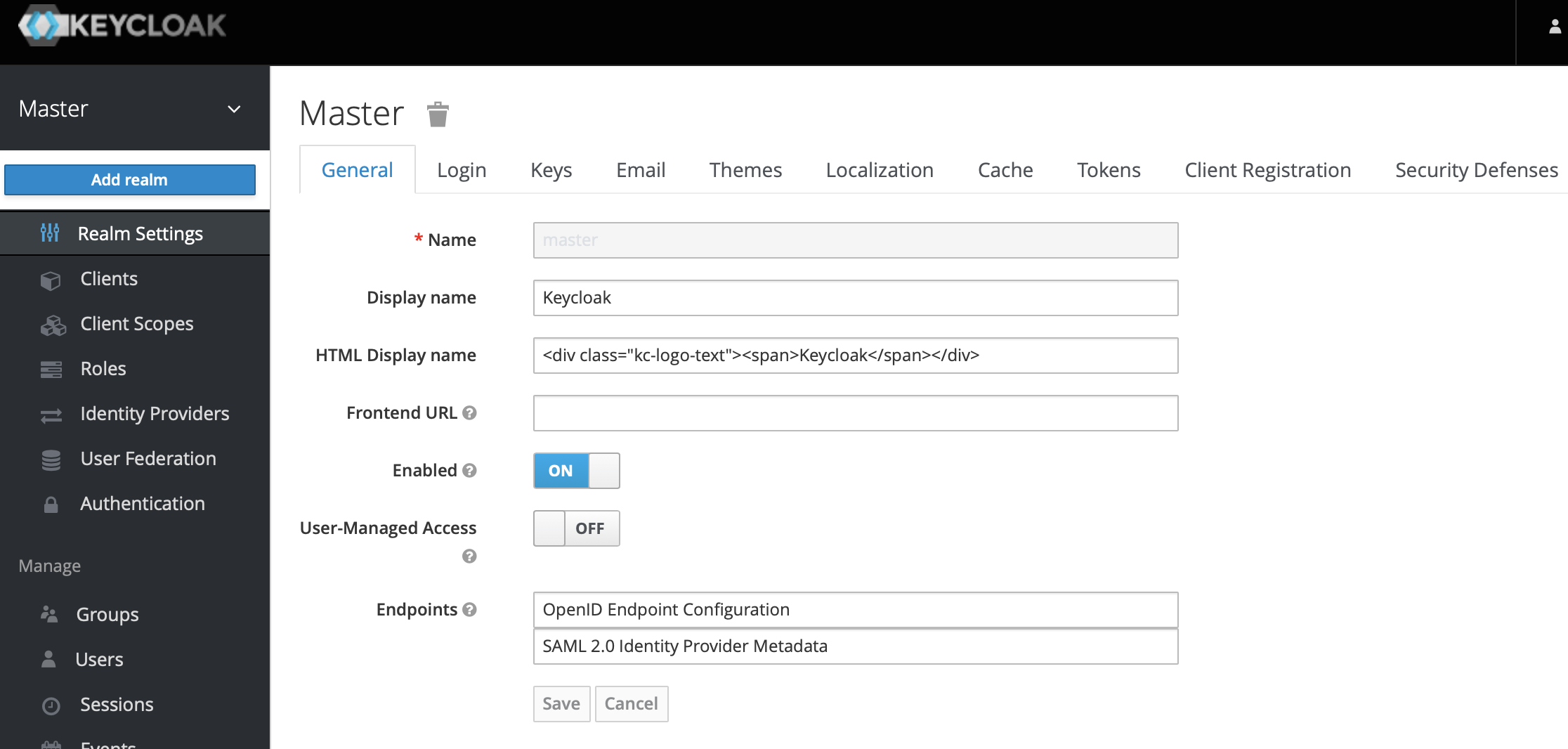
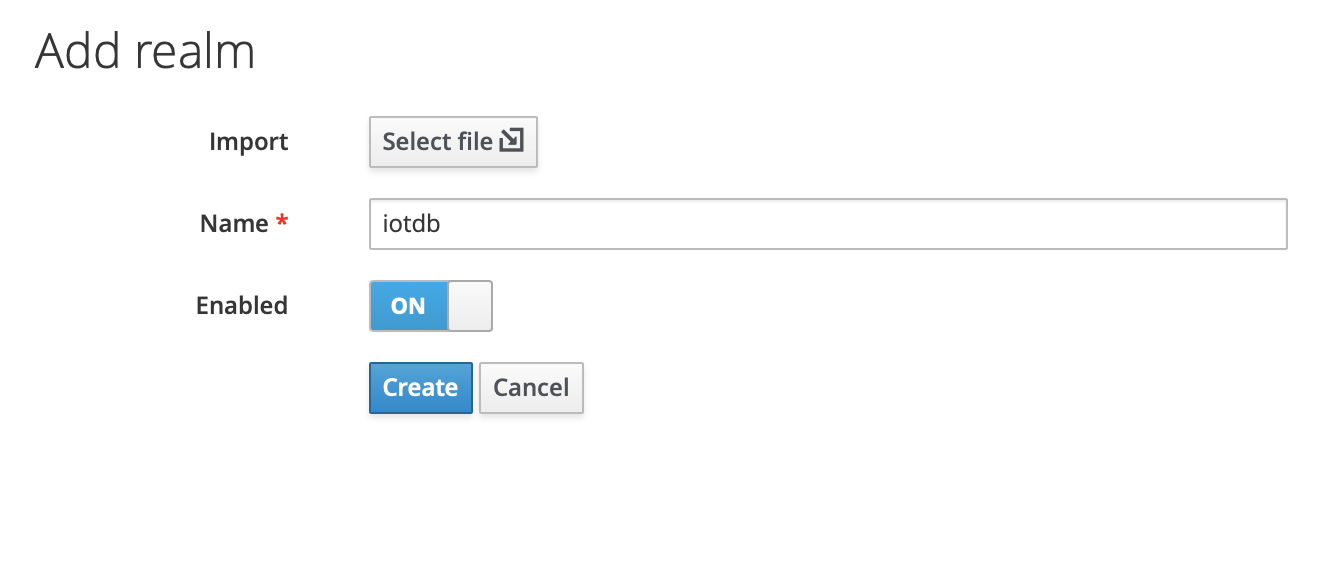
5、Click the menu clients on the left to create clients
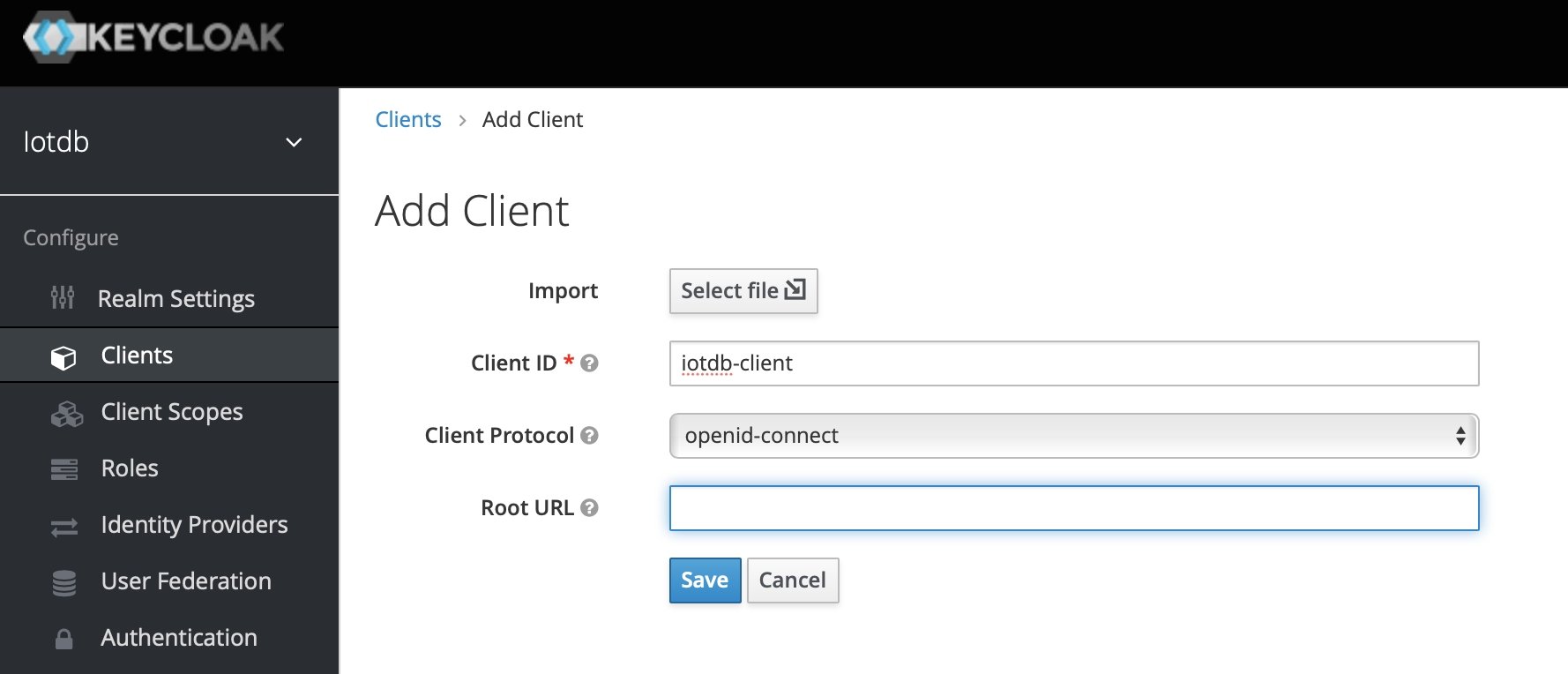
6、Click user on the left menu to create user
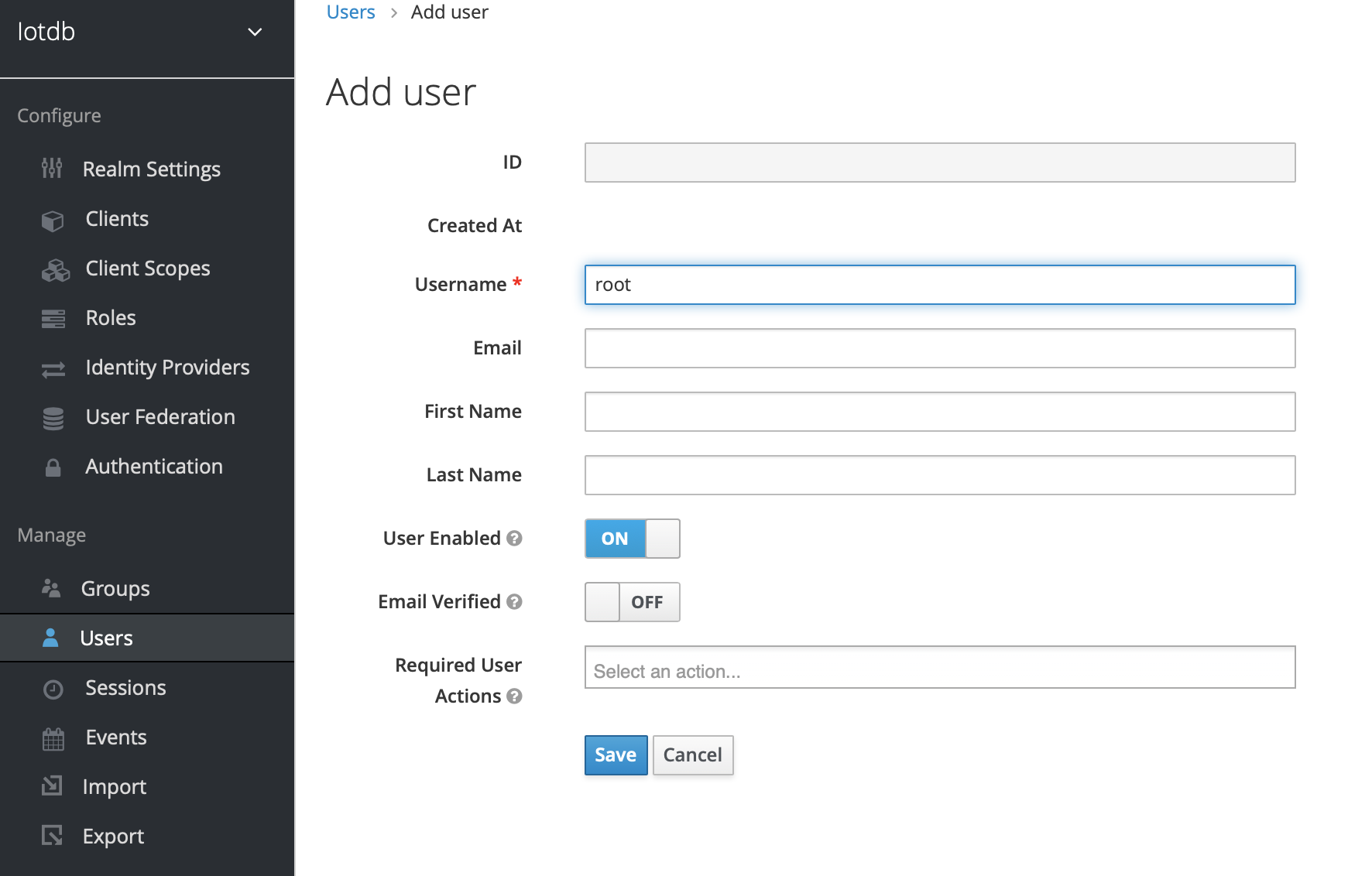
7、Click the newly created user ID, click the credentials navigation, enter the password and close the temporary option. The configuration of keycloud is completed
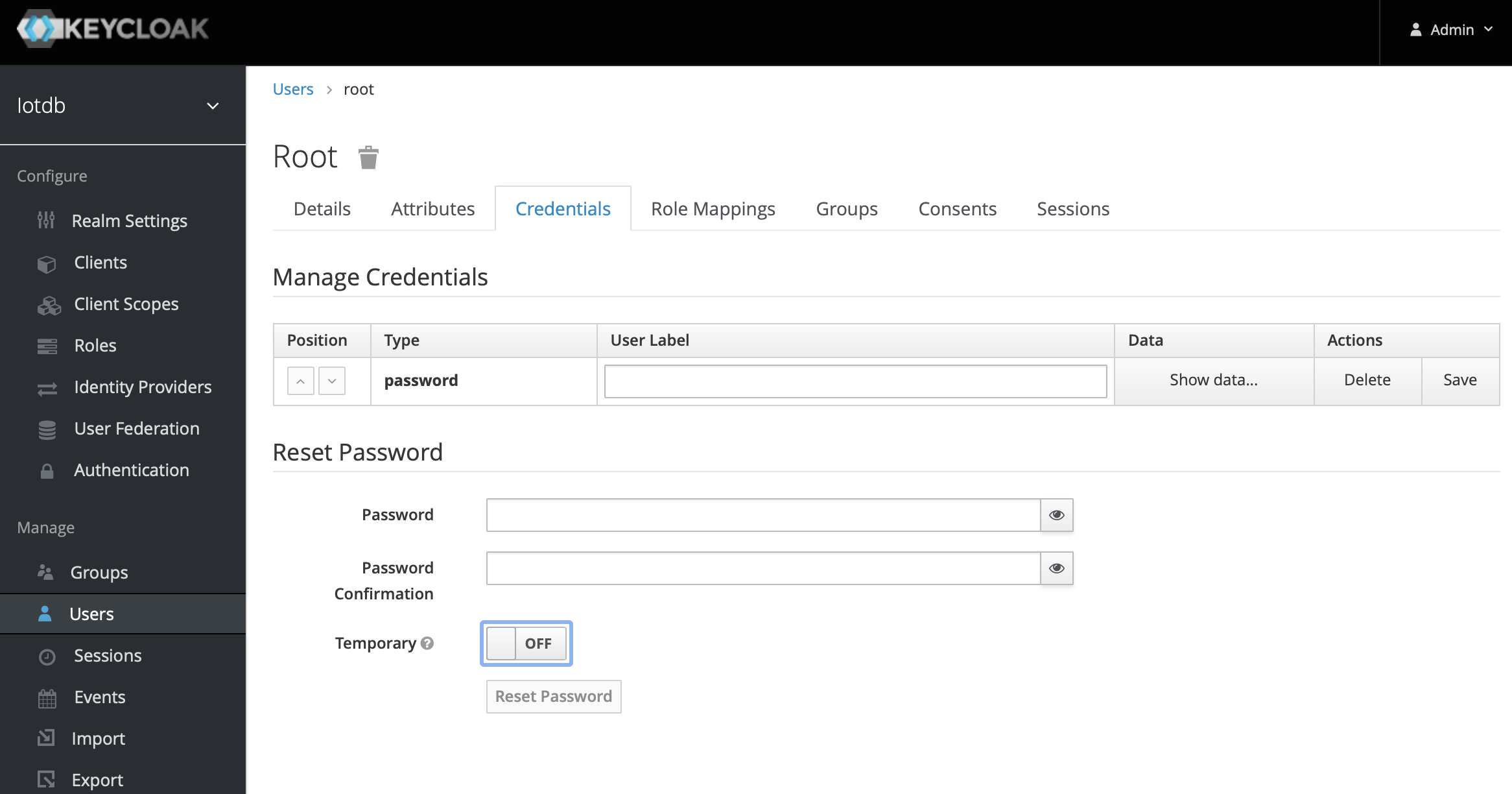
8、To create a role, click Roles on the left menu and then click the Add Role button to add a role
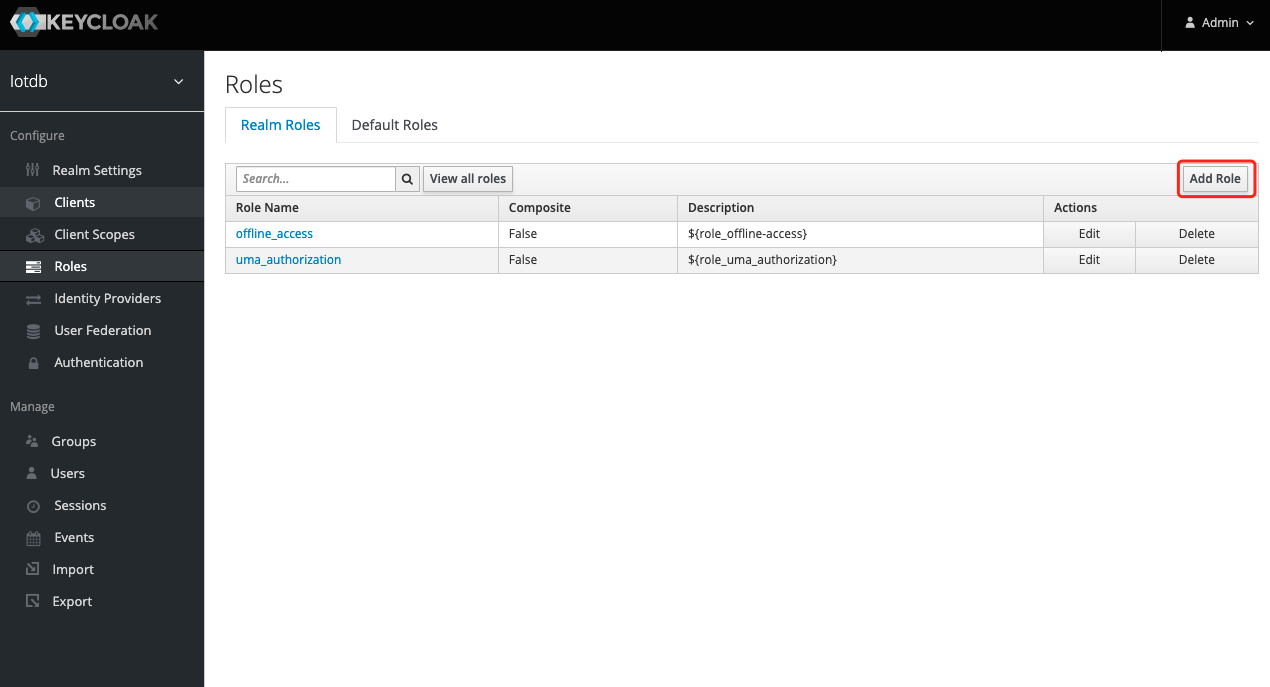
9、 Enter iotdb_admin in the Role Name and click the save button. Tip: iotdb_admin here cannot be any other name, otherwise even after successful login, you will not have permission to use iotdb's query, insert, create storage group, add users, roles and other functions
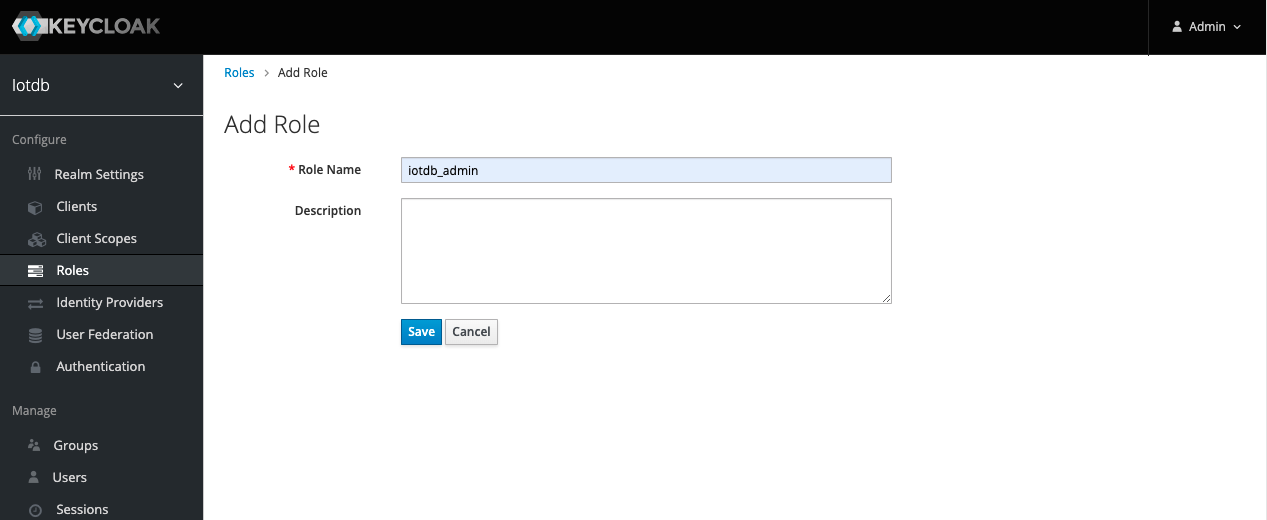
10、Click the User menu on the left and click the Edit button in the user list to add the iotdb_admin role we just created for this user
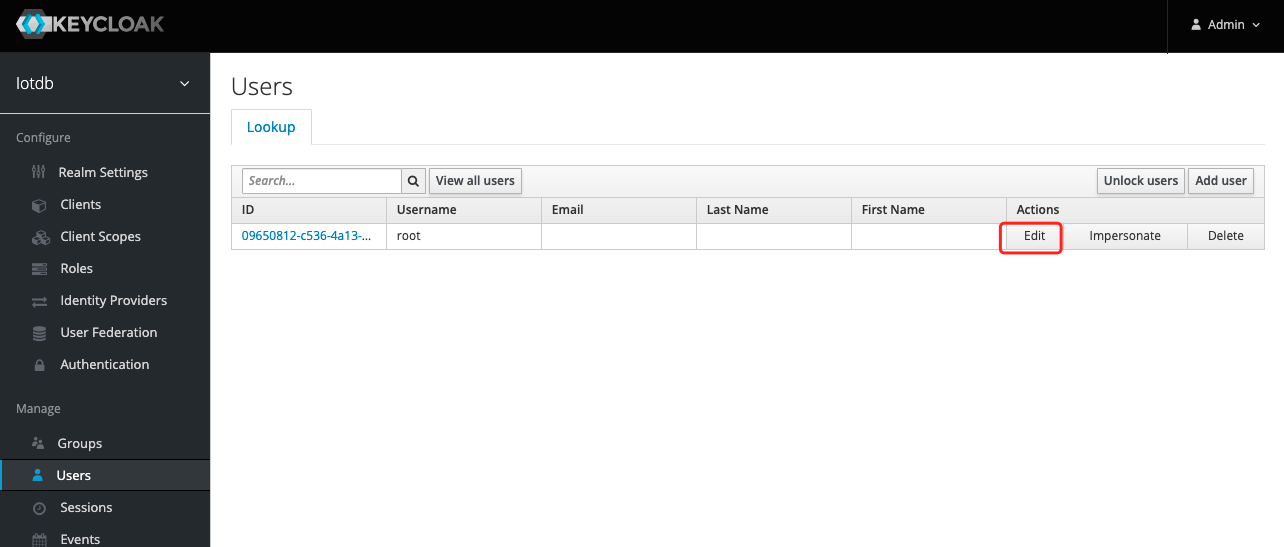
11、 Select Role Mappings, select the iotdb_admin role in Available Role and click the Add selected button to add the role
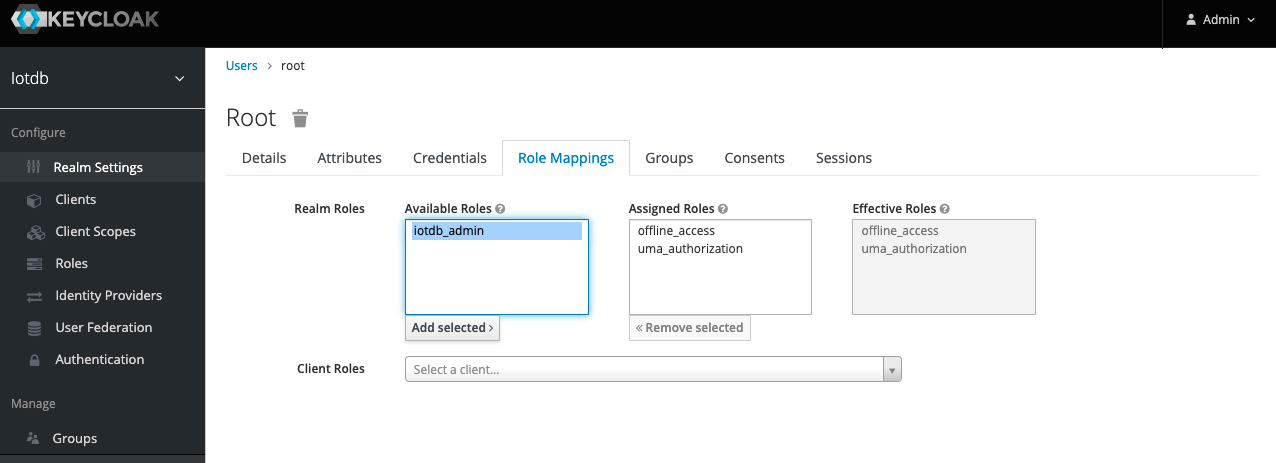
- If the
iotdb_adminrole is in Assigned Roles and theSuccess Role mappings updatedprompt appears, it proves that the role was added successfully
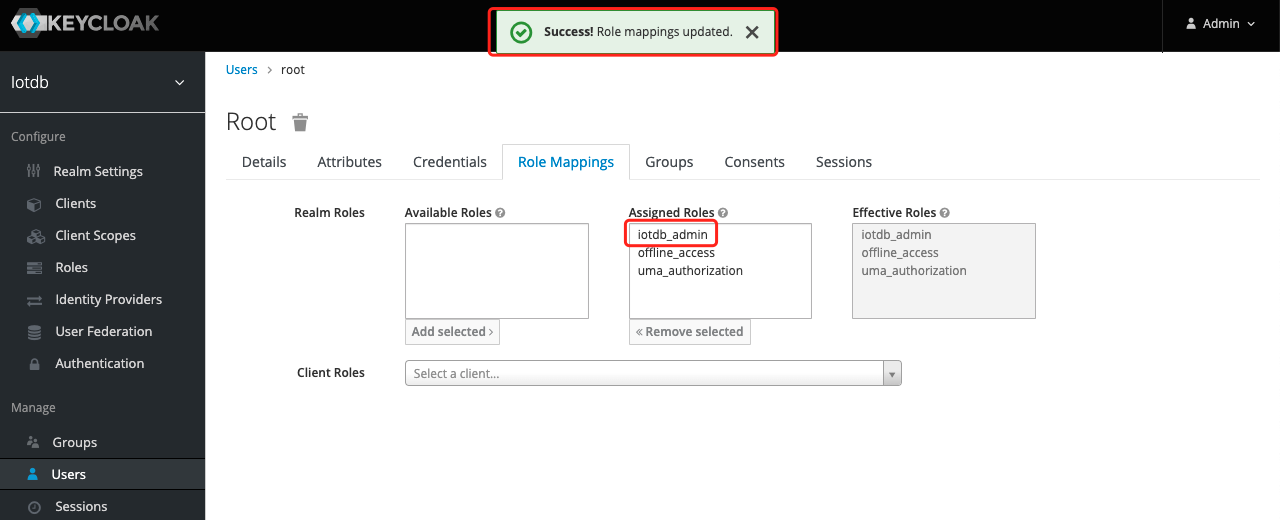
Tip: If the user role is adjusted, you need to regenerate the token and log in to iotdb again to take effect
The above steps provide a way for keycloak to log into iotdb. For more ways, please refer to keycloak configuration
If OIDC is enabled on server side then no username / passwort is needed but a valid Access Token from the OIDC Provider.
So as username you use the token and the password has to be empty, e.g.
Shell > sbin/start-cli.sh -h 10.129.187.21 -p 6667 -u {my-access-token} -pw ""Among them, you need to replace {my access token} (note, including {}) with your token, that is, the value corresponding to access_token.
How to get the token is dependent on your OpenID Connect setup and not covered here.
In the simplest case you can get this via the command line with the passwort-grant.
For example, if you use keycloack as OIDC and you have a realm with a client iotdb defined as public you could use
the following curl command to fetch a token (replace all {} with appropriate values).
curl -X POST "https://{your-keycloack-server}/auth/realms/{your-realm}/protocol/openid-connect/token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "username={username}" \
-d "password={password}" \
-d 'grant_type=password' \
-d "client_id=iotdb-client"The response looks something like
{"access_token":"eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJxMS1XbTBvelE1TzBtUUg4LVNKYXAyWmNONE1tdWNXd25RV0tZeFpKNG93In0.eyJleHAiOjE1OTAzOTgwNzEsImlhdCI6MTU5MDM5Nzc3MSwianRpIjoiNjA0ZmYxMDctN2NiNy00NTRmLWIwYmQtY2M2ZDQwMjFiNGU4IiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cDovL2F1dGguZGVtby5wcmFnbWF0aWNpbmR1c3RyaWVzLmRlL2F1dGgvcmVhbG1zL0lvVERCIiwiYXVkIjoiYWNjb3VudCIsInN1YiI6ImJhMzJlNDcxLWM3NzItNGIzMy04ZGE2LTZmZThhY2RhMDA3MyIsInR5cCI6IkJlYXJlciIsImF6cCI6ImlvdGRiIiwic2Vzc2lvbl9zdGF0ZSI6IjA2MGQyODYyLTE0ZWQtNDJmZS1iYWY3LThkMWY3ODQ2NTdmMSIsImFjciI6IjEiLCJhbGxvd2VkLW9yaWdpbnMiOlsibG9jYWxob3N0OjgwODAiXSwicmVhbG1fYWNjZXNzIjp7InJvbGVzIjpbIm9mZmxpbmVfYWNjZXNzIiwidW1hX2F1dGhvcml6YXRpb24iLCJpb3RkYl9hZG1pbiJdfSwicmVzb3VyY2VfYWNjZXNzIjp7ImFjY291bnQiOnsicm9sZXMiOlsibWFuYWdlLWFjY291bnQiLCJtYW5hZ2UtYWNjb3VudC1saW5rcyIsInZpZXctcHJvZmlsZSJdfX0sInNjb3BlIjoiZW1haWwgcHJvZmlsZSIsImVtYWlsX3ZlcmlmaWVkIjp0cnVlLCJwcmVmZXJyZWRfdXNlcm5hbWUiOiJ1c2VyIn0.nwbrJkWdCNjzFrTDwKNuV5h9dDMg5ytRKGOXmFIajpfsbOutJytjWTCB2WpA8E1YI3KM6gU6Jx7cd7u0oPo5syHhfCz119n_wBiDnyTZkFOAPsx0M2z20kvBLN9k36_VfuCMFUeddJjO31MeLTmxB0UKg2VkxdczmzMH3pnalhxqpnWWk3GnrRrhAf2sZog0foH4Ae3Ks0lYtYzaWK_Yo7E4Px42-gJpohy3JevOC44aJ4auzJR1RBj9LUbgcRinkBy0JLi6XXiYznSC2V485CSBHW3sseXn7pSXQADhnmGQrLfFGO5ZljmPO18eFJaimdjvgSChsrlSEmTDDsoo5Q","expires_in":300,"refresh_expires_in":1800,"refresh_token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJhMzZlMGU0NC02MWNmLTQ5NmMtOGRlZi03NTkwNjQ5MzQzMjEifQ.eyJleHAiOjE1OTAzOTk1NzEsImlhdCI6MTU5MDM5Nzc3MSwianRpIjoiNmMxNTBiY2EtYmE5NC00NTgxLWEwODEtYjI2YzhhMmI5YmZmIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cDovL2F1dGguZGVtby5wcmFnbWF0aWNpbmR1c3RyaWVzLmRlL2F1dGgvcmVhbG1zL0lvVERCIiwiYXVkIjoiaHR0cDovL2F1dGguZGVtby5wcmFnbWF0aWNpbmR1c3RyaWVzLmRlL2F1dGgvcmVhbG1zL0lvVERCIiwic3ViIjoiYmEzMmU0NzEtYzc3Mi00YjMzLThkYTYtNmZlOGFjZGEwMDczIiwidHlwIjoiUmVmcmVzaCIsImF6cCI6ImlvdGRiIiwic2Vzc2lvbl9zdGF0ZSI6IjA2MGQyODYyLTE0ZWQtNDJmZS1iYWY3LThkMWY3ODQ2NTdmMSIsInNjb3BlIjoiZW1haWwgcHJvZmlsZSJ9.ayNpXdNX28qahodX1zowrMGiUCw2AodlHBQFqr8Ui7c","token_type":"bearer","not-before-policy":0,"session_state":"060d2862-14ed-42fe-baf7-8d1f784657f1","scope":"email profile"}The interesting part here is the access token with the key access_token.
This has to be passed as username (with parameter -u) and empty password to the CLI.
Batch Operation of Cli
-e parameter is designed for the Cli/shell tool in the situation where you would like to manipulate IoTDB in batches through scripts. By using the -e parameter, you can operate IoTDB without entering the cli's input mode.
In order to avoid confusion between statements and other parameters, the current situation only supports the -e parameter as the last parameter.
The usage of -e parameter for Cli/shell is as follows:
The Linux and MacOS system commands:
Shell > sbin/start-cli.sh -h {host} -p {rpcPort} -u {user} -pw {password} -e {sql for iotdb}The Windows system commands:
Shell > sbin\start-cli.bat -h {host} -p {rpcPort} -u {user} -pw {password} -e {sql for iotdb}In the Windows environment, the SQL statement of the -e parameter needs to use `` to replace " "
In order to better explain the use of -e parameter, take following as an example(On linux system).
Suppose you want to create a storage group root.demo to a newly launched IoTDB, create a timeseries root.demo.s1 and insert three data points into it. With -e parameter, you could write a shell like this:
# !/bin/bash
host=127.0.0.1
rpcPort=6667
user=root
pass=root
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "set storage group to root.demo"
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "create timeseries root.demo.s1 WITH DATATYPE=INT32, ENCODING=RLE"
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "insert into root.demo(timestamp,s1) values(1,10)"
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "insert into root.demo(timestamp,s1) values(2,11)"
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "insert into root.demo(timestamp,s1) values(3,12)"
./sbin/start-cli.sh -h ${host} -p ${rpcPort} -u ${user} -pw ${pass} -e "select s1 from root.demo"The print results are shown in the figure, which are consistent with the cli and jdbc operations.
Shell > ./shell.sh
+-----------------------------+------------+
| Time|root.demo.s1|
+-----------------------------+------------+
|1970-01-01T08:00:00.001+08:00| 10|
|1970-01-01T08:00:00.002+08:00| 11|
|1970-01-01T08:00:00.003+08:00| 12|
+-----------------------------+------------+
Total line number = 3
It costs 0.267sIt should be noted that the use of the -e parameter in shell scripts requires attention to the escaping of special characters.
